The key driver behind the crowding out phenomenon is
A. a decrease in real GDP.
B. a decrease in the interest rate.
C. an increase in real GDP.
D. an increase in the interest rate.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Based on the figure below. Starting from long-run equilibrium at point C, an increase in government spending that increases aggregate demand from AD to AD1 will lead to a short-run equilibrium at point ________ creating _____gap. 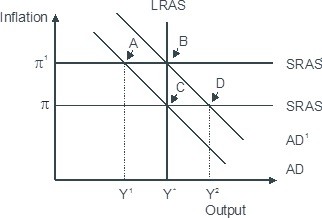
A. D; an expansionary B. B; no output C. B; expansionary D. A; a recessionary
A net capital inflow occurs in open economies where investment is:
A. higher than national savings. B. lower than national savings. C. equal to national savings. D. higher than national spending.
The aggregate supply curve is
a. generally flatter as the level of resource use rises. b. never vertical, even at full employment. c. relatively flat at low levels of output. d. relatively steep at low levels of output.
During the three years following the financial crisis of 2008,
a. the monetary base more than doubled and the M1 money supply increased even more rapidly. b. the monetary base more than doubled, but the M1 money supply increased much less rapidly. c. the monetary base fell by almost 50 percent, but the M1 money supply continued to grow at a steady rate. d. the monetary base fell by almost 50 percent, causing a sharp reduction in the M1 money supply.