The cost associated with foregoing the opportunity to employ a resource in its best alternative use is called:
A. an avoidable cost.
B. a sunk cost.
C. an opportunity cost.
D. the user cost of capital.
C. an opportunity cost.
You might also like to view...
Steve and Lee have been shipwrecked on a deserted island in the Hawaiian chain. Their economic activity consists of either gathering pineapples or fishing. We know Steve can catch four fish in one hour or harvest two baskets of pineapples. In the same
time Lee can reel in two fish or harvest two baskets of pineapples. If they each spend four hours a day fishing and four hours a day harvesting pineapples, how many of each will Steve produce? How many will Lee produce? What will their total production be? If Steve and Lee don't trade with each other, who is better off? Why? Assume Lee and Steve both operate on straight-line production possibilities curves. What is Steve's opportunity cost of producing a basket of pineapples? Of a producing a fish? What is Lee's opportunity cost of producing a basket of pineapples? Of a producing a fish? If Steve and Lee traded, who has the comparative advantage in fish? Pineapples? If Lee and Steve specialize in and trade the good in which they have a comparative advantage, how much of each good will be produced in an eight hour day? What are the gains from trade?
Profits or losses must be temporary for perfectly competitive firms. Why?
Which market adjusts the quickest in response to shocks to the economy?
A. The goods market B. The labor market C. The asset market D. The asset, labor, and goods markets adjust at about the same speed to eliminate a disequilibrium in the macroeconomy.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 4.4 below to answer the question(s) that follow.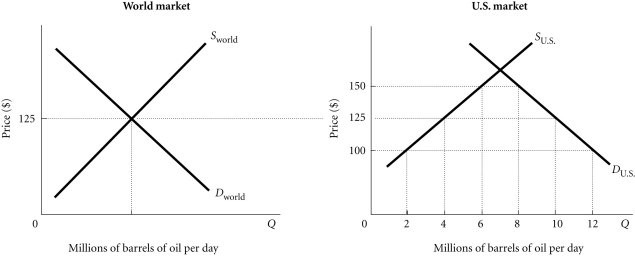 Figure 4.4Refer to Figure 4.4. Assume that initially there is free trade. If the United States then imposes a $25 tariff per barrel of imported oil, the tariff revenue generated will equal
Figure 4.4Refer to Figure 4.4. Assume that initially there is free trade. If the United States then imposes a $25 tariff per barrel of imported oil, the tariff revenue generated will equal
A. $25 million per day. B. $50 million per day. C. $100 million per day. D. $125 million per day.