Some nations use a currency board to manage their currencies. How does this work?
a. It is all in the hands of international banks.
b. The International Monetary Fund manages the currency.
c. There is a fixed rate regime with a set of strict rules and policy guidelines to keep the currency's value stable.
d. The currency is allowed to float, but its fluctuations are reviewed periodically by a board of economists.
Answer: c. There is a fixed rate regime with a set of strict rules and policy guidelines to keep the currency's value stable.
You might also like to view...
The figure below shows the demand curve, marginal revenue curve, marginal cost curve and average total cost curve for a monopolist. 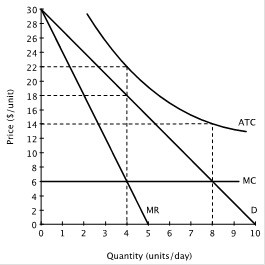 At this monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output, it:
At this monopolist's profit-maximizing level of output, it:
A. earns an economic profit of $16 per day. B. earns an economic profit of $64 per day. C. incurs an economic loss of $16 per day. D. incurs an economic loss of $64 per day.
In the figure above, at point A the consumer is willing to give up ________ pounds of pickles to get one additional pound of olives
A) 8 B) 6 C) 1 1/3 D) 2
In a small open economy, an increase in government spending, while taxes remain the same, will be accompanied by
A) a decrease in private investment and an increase in privates saving. B) an increase in private investment and a decrease in private savings. C) a decrease in national savings and an increase in foreign borrowing. D) an increase in national savings and a decrease in foreign borrowing.
If two investments are uncorrelated:
A. there is no benefit from diversification. B. there is no benefit to hedging. C. diversification reduces risk without changing the expected payoff. D. diversification reduces both risk and the expected payoff.