Profits are part of the
A. total income.
B. final consumer goods.
C. factor services.
D. monetary value of output.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
A major difference between a single-price monopolist and a perfectly competitive firm is that the
A) monopolist can maximize profit by setting the price of the output where demand is inelastic. B) monopolist can always increase its profits by increasing the price of its output. C) monopolist's marginal revenue is less than price. D) monopolist is guaranteed to earn an economic profit.
In the period 1960–95, the federal government
(a) played, in general, a much larger role in the economy during this period than prior to World War II. (b) played a small role in the economy, similar to the 1920s. (c) eliminated most of the major programs for the federal government that were established by the New Deal in the 1930s, while state and local governments began to play a larger role in the economy. (d) played a large role in defense spending but followed basically a laissez-faire policy toward the rest of the economy.
Beginning from full-employment equilibrium, illustrate graphically how each of the following would impact the economy
a. the short-run impact of an unanticipated decrease in the money supply b. the long-run impact of an unanticipated decrease in the money supply
A country has the per-worker production function yt = 6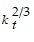 ,where yt is output per worker and kt is the capital-labor ratio. The depreciation rate is 0.1 and the population growth rate is 0.1. The saving function is St = 0.1Yt,where St is total national saving and Yt is total output.(a)What is the steady-state value of capital-labor ratio?(b)What is the steady-state value of output per worker?(c)What is the steady-state value of consumption per worker?
,where yt is output per worker and kt is the capital-labor ratio. The depreciation rate is 0.1 and the population growth rate is 0.1. The saving function is St = 0.1Yt,where St is total national saving and Yt is total output.(a)What is the steady-state value of capital-labor ratio?(b)What is the steady-state value of output per worker?(c)What is the steady-state value of consumption per worker?
What will be an ideal response?