This graph depicts the demand for a normal good.
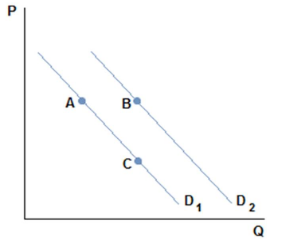
A shift from B to A in the graph shown might be caused by:
A. a decrease in the good's price.
B. an increase in the good's price.
C. a decrease in the price of a substitute.
D. an increase in the price of a substitute.
C. a decrease in the price of a substitute.
You might also like to view...
How does an increase in a country's exchange rate affect its balance of trade?
A) An increase in the exchange rate raises imports, reduces exports, and reduces the balance of trade. B) An increase in the exchange rate reduces imports, raises exports, and increases the balance of trade. C) An increase in the exchange rate raises imports, reduces exports, and increases the balance of trade. D) An increase in the exchange rate reduces imports, raises exports, and reduces the balance of trade.
If aggregate expenditure was less than GDP, which of the following would happen?
a. Inventories would shrink and GDP would drop in future periods. b. Inventories would grow and GDP would drop in future periods. c. Inventories would shrink and GDP would increase in future periods. d. Inventories would grow and GDP would increase in future periods. e. Inventories would not change and GDP would drop in future periods.
The concept of slope can be used to answer questions about how much one variable responds to changes in another variable
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
________ are costs that require a monetary payment.
A. Implicit costs B. Explicit costs C. Accounting costs D. Both Explicit costs and Accounting costs are correct.