The opportunity cost of current household consumption is the
a. wage rate.
b. market interest rate.
c. price of the goods consumed.
d. explicit cost of consumption.
b
You might also like to view...
Suppose a monopolist faces the demand curve shown below. 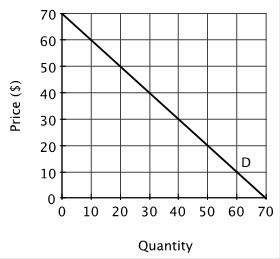 The monopolist maximizes its profits by:
The monopolist maximizes its profits by:
A. producing 35 units, since this is where total revenue is maximized. B. charging $70 for each unit. C. producing the level of output at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost. D. producing the level of output at which marginal revenue minus marginal cost is greatest.
According to the U.S. Secret Service, approximately $2.6 billion of U.S. paper currency in circulation is counterfeit. As long as counterfeit U.S. currency remains undetected and in circulation, an increase in the U.S
inflation rate would essentially A) decrease the real value of the counterfeit currency. B) increase the nominal value of the counterfeit currency. C) increase the real value of the counterfeit currency. D) decrease the nominal value of the counterfeit currency.
Gross domestic product can be calculated
A) either by valuing the nation's output of goods and services or by valuing the income generated in the production process. B) by adding up the personal consumption of all members of the society. C) by adding up the value of all intermediate goods used in the economy. D) by adding up the income tax returns of all members of the society.
Assume that at the current market price, a perfectly competitive firm's profit-maximizing level of output yields total revenues that are just equal to total costs. Which of the following statements applies to this firm?
A) The firm should shut down right now. B) The firm should continue to operate in the short run to minimize losses, but shut down if things don't improve over the long run. C) The firm is earning zero economic profit and should continue to operate. D) The firm should increase its explicit costs to reduce its tax burden.