Refer to the diagrams. The case of an inferior good is represented by figure:
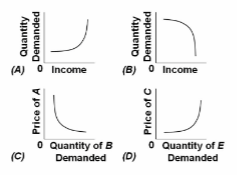
A. A.
B. B.
C. C.
D. D.
B. B.
You might also like to view...
The shape of a firm's expansion path depends upon
a. the price of the labor input. b. the price of the capital input. c. the shape of the firm's production function. d. all of these factors.
Suppose a consumer's expected utility function given two possible states of nature A and B can be expressed in terms of dollars worth of food consumption, F, in both states as U(FA, FB) = [0.6 × ln(FA)] + [0.4 × ln(FB)]. For this utility function, MUA is (0.6/FA) and MUB is (0.4/FB). Without insurance, the consumer can consume 200 in state A but only 50 in state B. The consumer can purchase insurance at a premium of 50 cents per dollar of benefit. How much insurance will she purchase?
A. $50 B. $150 C. $250 D. $416.67
Suppose a monopsonist must pay $10 per hour to attract 10 workers. If the same monopsonist must raise its wage to $11 per hour to attract the 11th worker, what is its marginal factor cost for labor?
A. $121 per hour. B. $11 per hour. C. $21 per hour. D. $10 per hour.
Number of workersUnits of output0012525539541255150Table 8.2Refer to Table 8.2, which gives a firm's production function. Assume that all non-labor inputs are fixed. The marginal product of the fifth worker is:
A. 0 units. B. 10 units. C. 25 units. D. 30 units.