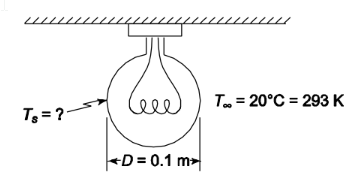
Only 10% of the energy dissipated by the tungsten filament of an incandescent lamp is in the form of useful visible light. Consider a 100 W lamp with a 10 cm spherical glass bulb. Assuming an emissivity of 0.85 for the glass and ambient air temperature of 20°C, what is the temperature of the glass bulb?
GIVEN
• A spherical glass light bulb in air
• Bulb power consumption (P) = 100 W
• 10% of energy is in the form of visible light
• Diameter (D) = 10 cm = 0.1 m
• Bulb emissivity (?) = 0.85
• Ambient temperature (T?) = 20°C = 293 K
FIND
• The temperature of the glass bulb (Ts)
ASSUMPTIONS
• Ambient air is till
• The bulb has reached steady state
• The surrounding behave as a black body at T?
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
Boltzmann constant (?) = 5.7 × 10–8 W/(m2 K4).
The rate of heat transfer by convection and radiation from the bulb must equal the rate of heat generation.
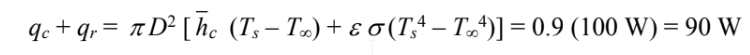
Since the fluid properties depend on the surface temperature, an iterative procedure must be used. For the first iteration, let Ts = 100°C = 373 K.
for dry air at the mean temperature of 60°C
Thermal expansion coefficient (?) = 0.00300 1/K
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.0279 W/(m K)
Kinematic viscosity (?) = 19.4 × 10–6 m2/s
Prandtl number (Pr) = 0.71
The characteristic length for a 3-D body is given
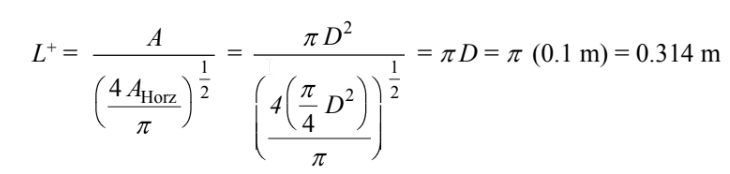
The Grashof and Rayleigh numbers are
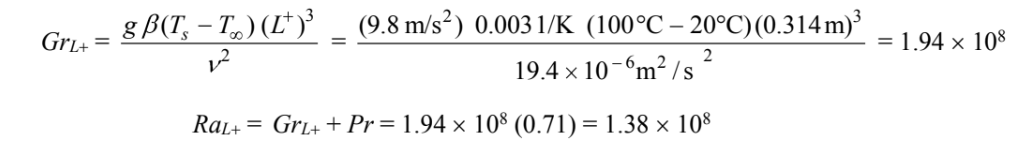
correlates data for 3-D bodies including spheres for 200 < RaL+ < 1.5 × 109
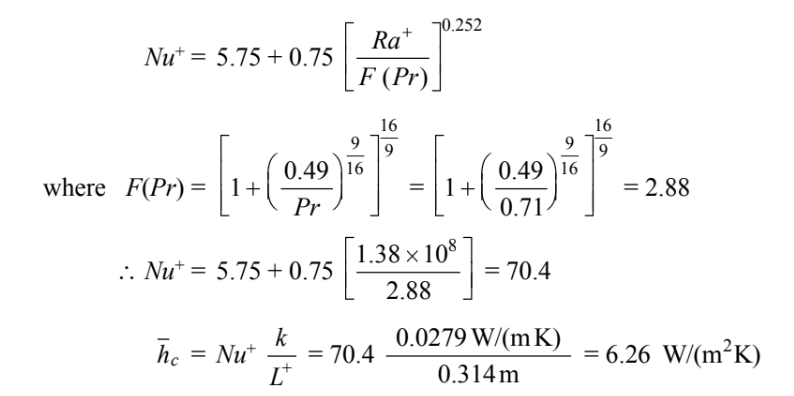
The rate of heat transfer by convection and radiation must equal the heat generation rate
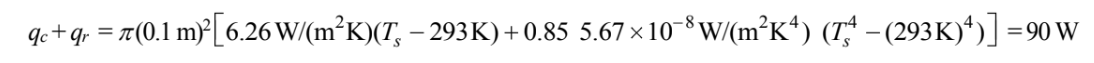
Checking the units then eliminating them for clarity
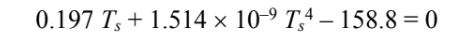
By trial and error: Ts = 460 K = 187°C.
The results of further iterations are tabulated below
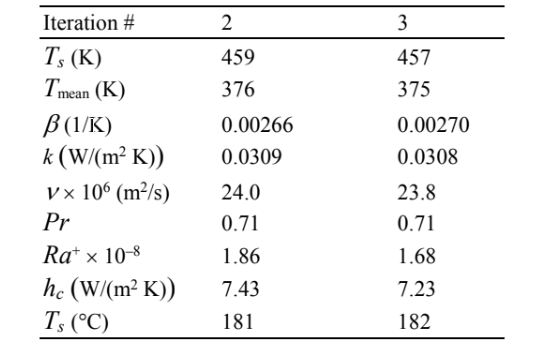
The bulb temperature, therefore, is approximately 182°C.
COMMENTS
Note that radiative transfer accounts for about 66% of the total heat transfer from the bulb.
You might also like to view...
Observations of the tiny irregularities in the cosmic microwave background support the idea that the Universe
A. will continue to expand forever. B. will collapse in the distant future. C. is composed primarily of matter, rather than antimatter. D. contains no dark matter. E. is composed primarily of neutrinos.
A device that measures absolute air pressure is called a barometer
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
RC Circuits: A charged capacitor is connected in series with a resistor and an open switch. At time t = 0 s, the switch is closed. Which of the graphs below best describes the current I through the resistor as a function of time t?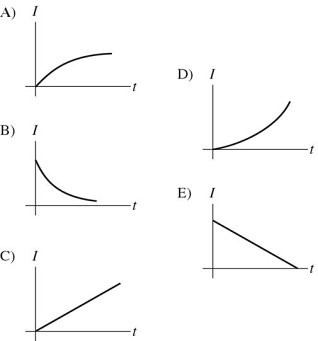
A. A B. B C. C D. D E. E
A hydrogen bomb may be approximated by a fireball at a temperature of 7200 K according to a report published in 1950 by the Atomic Energy Commission. (a) Calculate the total rate of radiant-energy emission in watts, assuming that the gas radiates as a blackbody and has a diameter of 1.5 km, (b) If the surrounding atmosphere absorbs radiation below 0.3 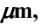 determine the per cent of the total radiation emitted by the bomb that is absorbed by the atmosphere, (c) Calculate the rate of irradiation on a 1 m2 area of the wall of a house 40 km from the center of the blast if the blast occurs at an altitude of 16 km and the wall faces in the direction of the blast, (d) Estimate the total amount of radiation absorbed
determine the per cent of the total radiation emitted by the bomb that is absorbed by the atmosphere, (c) Calculate the rate of irradiation on a 1 m2 area of the wall of a house 40 km from the center of the blast if the blast occurs at an altitude of 16 km and the wall faces in the direction of the blast, (d) Estimate the total amount of radiation absorbed
assuming that the blast lasts approximately 10 sec and that the wall is covered by a coat of red paint, (e) If the wall were made of oak whose flammability limit is estimated to be 650 K and that had a thickness of 1 cm, determine whether or not the wood would catch on fire. Justify your answer by an engineering analysis stating carefully all assumptions.
GIVEN
- A hydrogen bomb fireball
- Fireball temperature (T1) = 7200 K
- Surrounding atmosphere absorbs radiation below 0.3

- The blast occurs at an altitude (H) of 16 km = 16,000 m
FIND
(a) The total rate of radiant-energy emission in watts (qr)
(b) The per cent of the total radiation absorbed by te atmosphere
(c) The rate of irradiation on a 1 m2 area of the wall of a house 40 km (40,000 m) from the center of the blast and facing the blast (G2)
(d) Total amount of radiation absorbed if the blast lasts 10 seconds and the wall is covered with red paint
(e) If the walls are oak with a flammability limit of 650 K and a thickness (s) of 1 cm, will the wood catch fire?
ASSUMPTIONS
- The gas radiates as a blackbody
- Diameter of the fireball (D) = 1.5 km
- The air and surrounding temperature (T?) = 10°C
- The surroundings behave as a blackbody enclosure
- The heat transfer from the oak walls to its surroundings during the 10 seconds of irradiation can be neglected
- The house wall is initially at the surroundings temperature
SKETCH
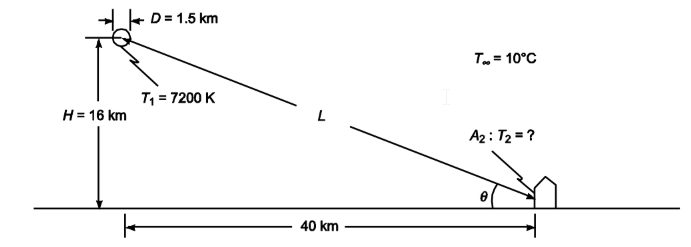
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
the Stephan-Boltzmann constant
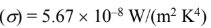
the emissivity of red paint at short wavelengths
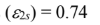
the emissivity of red paint at long wavelengths
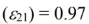
Specific heat
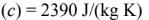
Thermal conductivity
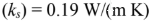
Density
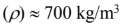
Thermal diffusivity