How are intermediate goods treated in the calculation of GDP?
A) Their value is counted separately, and their value is also included as part of the value of the final good for which they are an input.
B) Their value is counted separately, but is not included as part of the value of the final good for which they are an input.
C) They are included only if they are imported.
D) Their value is not counted separately, but included as part of the value of the final good for which they are an input.
D
You might also like to view...
A dominant strategy is:
A. when one strategy is chosen by a firm first and determines the best strategies of the other players that follow. B. when one strategy is chosen and cannot be changed without making at least one of the players worse off. C. when one strategy is always the best for a player to choose, regardless of what other players do. D. None of these statements is true.
A decrease in the availability of an important major resource such as oil shifts
a. aggregate supply right. b. aggregate supply left. c. aggregate demand right. d. aggregate demand left.
For a competitive firm, the value of the marginal product:
A. increases for each additional worker. B. remains constant across workers. C. is zero when profits are maximized. D. decreases for each additional worker.
Refer to the diagram. The general agreement of most economists is that the U.S. economy today is:
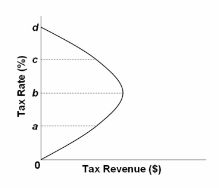
A. at b.
B. at some level below b.
C. at some level above b.
D. at d.