Exhibit 9-3 A monopolistic competitive firm in the long run
?
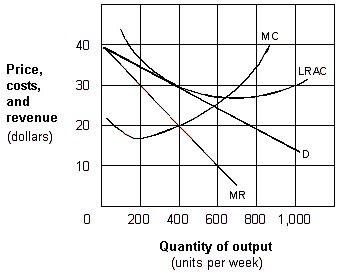
As presented in Exhibit 9-3, the long-run profit-maximizing output for the monopolistic competitive firm is:
A. zero units per week.
B. 200 units per week.
C. 400 units per week.
D. 600 units per week.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
If an individual's supply of labor curve is positively sloped throughout, then
a. the substitution effect always dominates the income effect. b. the income effect always dominates the substitution effect. c. the substitution effect dominates at low real wage levels and the income effect dominates at high real wage levels. d. the income effect dominates at low real wage levels and the substitution effect dominates at high real wage levels.
International reserves are
a. foreign exchange held by governments only b. foreign exchange held by central banks only c. foreign exchange held by governments or central banks d. gold only e. various internationally acceptable assets
Suppose that a worker in Agland can produce either 10 units of organic grain or 2 units of incense per year, and a worker in Zenland can produce either 5 units of organic grain or 15 units of incense per year. There are 20 workers in Agland and 10 workers in Zenland. Currently the two countries do not trade. Agland produces and consumes 100 units of grain and 20 units of incense per year. Zenland
produces and consumes 50 units of grain and no incense per year. If each country made the decision to specialize in producing the good in which it has a comparative advantage, then the combined yearly output of the two countries would increase by a. 30 units of grain and 100 units of incense. b. 30 units of grain and 150 units of incense. c. 50 units of grain and 90 units of incense. d. 50 units of grain and 130 units of incense.
Price discrimination is more likely in the case of services than in the case of goods because
A) producers of goods usually do not face downward sloping demand curves. B) it is easier to distinguish customers with different elasticities of demand with respect to services than with goods. C) elasticities of demand vary more with services than with goods. D) it is more difficult to resell services.