Discuss long-distance migration of sockeye salmon and ruby-throated hummingbirds with respect to stimulus for migration, metabolic preparation, feeding during migration, and metabolism during migration
What will be an ideal response?
Answer: Sockeye salmon grow and mature in the ocean and their migration to freshwater streams/rivers, where they were born, is seasonal and stimulated by reproductive maturity. To prepare for migration, the salmon fatten up and store most of the energy needed for migration as lipid or fat. Salmon do not feed during migration; they rely totally on their energy reserves. The advantage of not feeding on route means salmon do not need to utilize any time searching for food and avoid the risk of predation while feeding.
Ruby-throated hummingbird's migration south to wintering grounds is stimulated by photoperiod. Hummingbirds, like many migrating animals, store fat for migration because fat has a high energetic density. Unlike sockeye salmon, hummingbirds require more energy for migration than they can store, and as a result, they need to feed along their migration route.
You might also like to view...
The mean arterial pressure (MAP) is important because
A) it reflects the difference in time that systole lasts compared to diastole. B) it forces the practitioner to do math, thus they must pay attention to the values obtained. C) it represents the driving pressure for blood flow. D) it represents the driving pressure for blood flow and it reflects the difference in time that systole lasts compared to diastole. E) All of the answers are correct.
All cellular activities and metabolic reactions are controlled by ________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
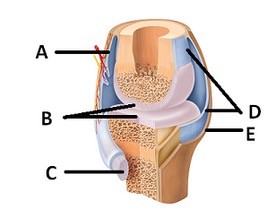 What does structure "A" represent on the diagram?
What does structure "A" represent on the diagram?
A. Tendon B. Fibrous capsule C. Articular cartilage D. Synovial membrane E. Bursa
An inborn error in lipid metabolism may cause all of the following symptoms EXCEPT ________.
A. liver and spleen enlargement from triglyceride accumulation B. atherosclerosis C. increased reliance on free fatty acids for energy production D. high blood cholesterol