When the price of raisins falls, the quantity of raisins demanded rises. Explain this change in terms of income and substitution effects
What will be an ideal response?
When the price of raisins falls, households have more purchasing power than before. If raisins are a normal good, this means that they will consume more of them. This is the income effect. Also, a decrease in the price of raisins makes raisins relatively less expensive. Thus, households will shift toward purchasing raisins from purchasing relatively more expensive goods. This is the substitution effect. Both effects imply that the quantity of raisins demanded will rise as the price of raisins falls.
You might also like to view...
If revenue in the short run is sufficient to offset variable costs but not all fixed costs, what should the firm do?
What will be an ideal response?
Under the Social Security program currently in existence
A) benefits are based on need. B) benefits are determined by whether or not one contributed to the system. C) benefits are provided to everyone who contributed to the system EXCEPT those under private retirement programs that provide an annual income in excess of $13,500. D) benefits are guaranteed to be no lower for future retirees than for current retirees.
Assume that the central bank sells government securities in the open market. If the nation has highly mobile international capital markets and a fixed exchange rate system, what happens to the real exchange rate and monetary base in the context of the Three-Sector-Model? State your answer after the macroeconomic system returns to complete equilibrium. Assume the nominal exchange rate is stated
as: (Foreign currency/ Domestic currency). a. The real exchange rate rises and monetary base rises. b. The real exchange rate rises and monetary base falls. c. The real exchange rate and monetary base fall. d. The real exchange rate and monetary base remain the same. e. There is not enough information to determine what happens to these two macroeconomic variables.
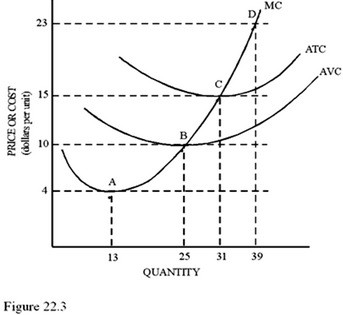 Refer to Figure 22.3 for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is $10,
Refer to Figure 22.3 for a perfectly competitive firm. If the market price is $10,
A. The firm should produce 31 units. B. The firm will shut down in the short run. C. The firm will earn normal profits. D. An economic loss will occur.