Define the following terms:
a. Axial pump
b. Centrifugal pump
c. Diaphragm pump
d. Dynamic pump
e. Positive displacement pump
f. Rotary pump
g. Screw pump
h. Vane pump
i. Cavitation
j. Impeller
k. Lobe pump
l. Piston pump
m. Priming
n. Pump performance curve
o. Seal
p. Vanes
q. Viscosity
r. Volute
a. An axial pump is a dynamic pump that uses a propeller or row of blades to propel liquids along the shaft.
b. A centrifugal pump is a type of dynamic pump that uses an impeller on a rotating shaft to generate pressure and move liquids.
c. A diaphragm pump is a mechanically or air-driven positive displacement reciprocating pump that consists of two flexible diaphragms connected by a common shaft.
d. A dynamic pump is a type of pump that converts the spinning motion of a blade or impeller into dynamic pressure to move liquids.
e. A positive displacement pump is a type of pump that uses pistons, diaphragms, gears, or screws to deliver a constant volume with each stroke.
f. A rotary pump is a type of positive displacement pump that moves in a circular motion to move liquids by trapping them in a specific area of a screw or a set of lobes, gears, or vanes.
g. A screw pump is a type of positive displacement rotary pump that displaces liquid with a screw.
h. A vane pump is a type of positive displacement rotary pump having either flexible or rigid vanes designed to displace liquid.
i. Cavitation is a condition inside a pump in which the liquid being pumped partially vaporizes due to variables such as temperature and pressure drop, and the resulting vapor bubbles and then implodes.
j. An impeller is a device with vanes that spins a liquid rapidly in order to generate centrifugal force.
k. A lobe pump is a type of positive displacement rotary pump consisting of a single or multiple lobes.
j. An impeller is a device with vanes that spins a liquid rapidly in order to generate centrifugal force.
k. A lobe pump is a type of positive displacement rotary pump consisting of a single or multiple lobes.
l. A piston pump is a type of positive displacement reciprocating pump that uses a piston inside a cylinder to move fluids.
m. Priming is the process of filling the suction line and casing of a pump with liquid to remove vapors and eliminate the tendency for it to become vapor bound or to lose suction.
n. A pump performance curve is a specification that describes the capacity, speed, horsepower, and head needed for correct pump operations.
o. A seal is a device that holds lubricants and process fluids in place while keeping out foreign materials where a rotating shaft passes through a pump casing.
p. Vanes are raised ribs on the impeller of a centrifugal pump designed to accelerate a liquid during impeller rotation.
q. Viscosity is the degree to which a liquid resists flow under applied force (for example, molasses has a higher viscosity than water at the same temperature).
r. A volute is a widened spiral casing in the discharge section of a centrifugal pump designed to convert liquid speed to pressure without shock.
You might also like to view...
Describe the importance of Portland cement in mortar.
What will be an ideal response?
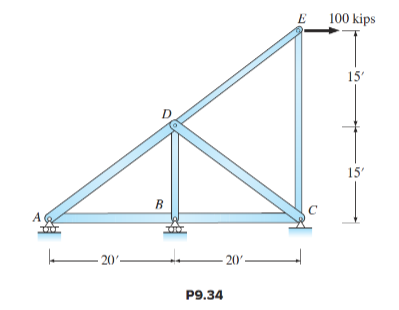
Consider the truss in Figure P9.34 without the applied loads. Determine the reactions and all bar forces for the truss if supports A and C settle by 0.25 in.
An ideal calving interval for the entire herd is near:
A. 11.5 to 12.0 months B. 12.5 to 13.0 months C. 13.5 to 14.0 months
In series circuits, the _____ is the same at any point in the circuit.
A. resistance B. current C. voltage drop