You want to produce a casting of sterling silver that is silver plus 13 atomic % copper. Pure silver is too soft for many applications, and adding 13 atomic % copper strengthens the silver without significantly changing the color. To produce the sterling silver casting, you are going to melt commercially pure silver and copper in a furnace, and then you will pour the liquid metal mixture into a mold. The following questions relate to this alloy.
(a) In selecting a furnace, what must be the minimum value of the high-temperature capability of your selected furnace?
(b) In transferring the liquid metal from the furnace to the mold, what is the minimum temperature that the metal can reach so that none of the metal has solidified?
(c) After the casting has cooled to room temperature, what phases are present, what is the equilibrium chemical composition (Ci) of each phase present, and what is the atom fraction (fi) of each phase present?
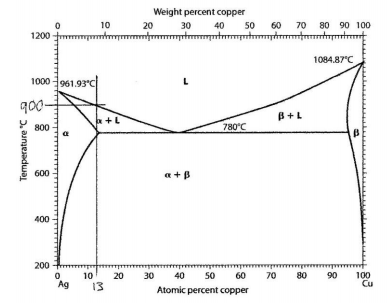
(a) The furnace should be able to melt any of the possible materials present including pure copper that melts at 1085°C.
(b) The first solid ? will form at 900°C, the melt must be above this temperature when poured.
(c) After the casting has cooled to room temperature the phases present are ? and ?. The equilibrium chemical composition of each phase present that the ? phase is pure silver and the ? phase is pure copper. The atom fraction (fi) of each phase present is
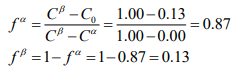
You might also like to view...
A 200 g hockey puck is launched up a metal ramp that is inclined at a 30° angle. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the puck and the ramp are µs = 0.40 and µk = 0.30,
and the puck's initial velocity at the base is 3.8 m/s parallel to the sloping surface of the ramp. What speed does the puck have when it slides back down to its starting point?
A very large sheet of a conductor carries a uniform charge density of 4.00 pC/mm2 on its surfaces. What is the electric field strength 3.00 mm outside the surface of the conductor? (?0 = 8.85 × 10-12 C2/N ? m2)
A) 4.52 × 105 N/C B) 2.26 × 105 N/C C) 9.04 × 105 N/C D) 0.226 N/C E) 0.452 N/C
The photosphere is the coolest layer close to the Sun, for the radiation of visible light allows it to cool off efficiently
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
A spaceship is observed by a stationary observer to be moving at 0.600 c. A laser beam is shown straight ahead from the front of the spaceship. How fast does the laser beam travel relative to the observer?
A. 1.60 c B. 1.36 c C. 1.00 c D. 0.640 c E. 0.360 c