Which of the following describes the light that can be detected from a person?
A) The person emits a few narrow wavelengths of visible light according to their composition.
B) The person emits many wavelengths of visible light and reflects a continuum of wavelengths of infrared light.
C) The person reflects many wavelengths of visible light and emits a continuum of wavelengths of infrared light.
D) The person absorbs a few narrow wavelengths of visible light according to their composition.
C
You might also like to view...
Energy Conservation With Conservative Forces: A bead is moving with a speed of 20 m/s at position A on the track shown in the figure. This track is friction-free, and there is no appreciable air resistance. What is the speed of the bead at point C?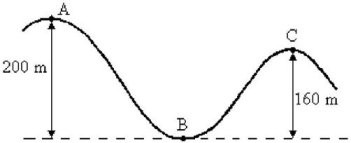
A. 0 m/s B. 34 m/s C. 69 m/s D. 20 m/s E. We cannot solve this problem without knowing the mass of the bead.
When an object is in translational equilibrium, which of these statements is not true?
A. the vector sum of the forces acting on the object is zero B. the object must be stationary C. the object has a constant velocity D. the speed of the object is a constant
Suppose that we suddenly discovered that all these years we'd been wrong about the distance from Earth to the Sun, and it is actually 10% greater than we'd thought. How would that affect our estimate of the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy?
A) It would not have any effect on our estimate of the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy. B) It would mean the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy is also 10% greater than we thought. C) It would mean the distance to the Andromeda Galaxy is 10% less than we thought. D) It would mean that all the objects we've assumed are standard candles really are not good standard candles, and therefore that we have no idea of the true distance to the Andromeda Galaxy.
At t = 0, a wheel rotating about a fixed axis at a constant angular acceleration of ?0.40 rad/s2 has an angular velocity of 1.5 rad/s and an angular position of 2.3 rad. What is the angular position of the wheel at t = 2.0 s?
A. 4.9 rad B. 4.7 rad C. 4.5 rad D. 4.3 rad E. 4.1 rad