The "rule of reason"
a. applies to business practices that are illegal regardless of their economic rationale or their consequences
b. applies to business practices that are legal, regardless of their consequences
c. means that business practices cannot be proven to be illegal, and a consent decree is required to halt the practices
d. considers why a certain business practice was adopted and what the effects on competition are, before determining whether the practice is illegal
e. focuses on market structure rather than on the behavior of firms in determining whether antitrust violations have occurred
D
You might also like to view...
One reason Zimbabwe suffered from hyperinflation is that the government had decided to pay for all of its expenses by
A) selling Treasury bonds to foreign governments. B) selling its government-run oil company to a private company, which then defaulted on its payment. C) raising interest rates to attract foreign direct investment, then nationalizing the foreign-owned facilities. D) printing more and more money.
Suppose bad weather in Florida unexpectedly results in a much smaller citrus crop than had been projected. The reduction in the supply of Florida citrus fruit would tend to
A) shift the supply curve for Florida citrus fruit down and to the right. B) increase the price of Florida citrus fruit. C) increase the supply of California citrus fruit. D) decrease the price of California citrus fruit.
Which of the following is not considered investment?
A. the construction of a new factory B. the purchase of government bonds C. the acquisition of capital goods D. the increase in planned inventories
Refer to the diagram for a monopolistically competitive producer. If this firm were to realize productive efficiency, it would:
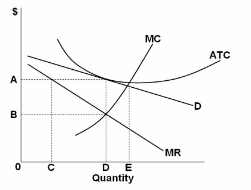
A. also realize an economic profit.
B. incur a loss.
C. also achieve allocative efficiency.
D. have to produce a smaller output.