Moral hazard and adverse selection are both examples of
a. the principal-agent problem.
b. externalities in consumption.
c. efficiency in markets.
d. perfect information.
e. asymmetric information.
E
You might also like to view...
The value of all final goods and services produced during a given time period measures a nation's
A) net exports. B) net national product. C) consumer price index. D) gross domestic product.
Most of the pressure for a monetary growth rule has disappeared because since 1980
A) the relationship between movements in interest rates and movements in real GDP and the price level have become much weaker. B) the relationship between movements in the money supply and movements in real GDP and the price level have become much stronger. C) the relationship between movements in the money supply and movements in real GDP and the price level have become much weaker. D) the relationship between movements in interest rates and movements in real GDP and the price level have become much stronger.
The term ceteris paribus means
A) the greatest good for all. B) the study of scarcity and choice. C) all other things remaining constant or equal. D) value-free and testable.
Figure 11-3
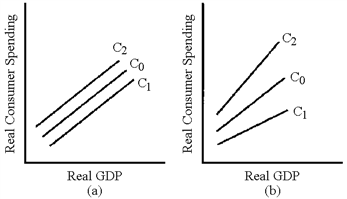
In Figure 11-3, which line represents the change in the consumption schedule caused by a cut in fixed taxes?
a.
C1 in graph (a)
b.
C2 in graph (a)
c.
C1 in graph (b)
d.
C2 in graph (b)