Refer to the diagram. The decline in price from P 1 to P 2 will:
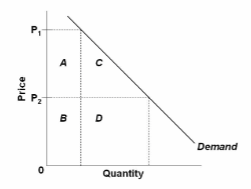
A. increase total revenue by D.
B. increase total revenue by B + D.
C. decrease total revenue by A.
D. increase total revenue by D - A.
D. increase total revenue by D - A.
You might also like to view...
The above table gives the total cost schedule for oil changes at the local Jiffy Lube
a. What is Jiffy Lube's total fixed cost? b. What is the total variable cost of 2 oil changes? c. What is the average variable cost of 4 oil changes? d. What is the average fixed cost of 2 oil changes? e. What is the marginal cost of the 3rd oil change?
Why is the Big Mac a good indicator of purchasing power parity?
What will be an ideal response?
The text calls the type of comparative advantage that is not easily changed, such as climate:
A. inherent comparative advantage. B. stable comparative advantage. C. permanent comparative advantage. D. equilibrium comparative advantage.
In perfect competition
A) the market demand curve and the individual's demand curve are identical. B) the market demand curve is perfectly inelastic while demand for an individual seller's product is perfectly elastic. C) the market demand curve is perfectly elastic while demand for an individual seller's product is perfectly inelastic. D) the market demand curve is downward sloping while demand for an individual seller's product is perfectly elastic.