A good salesperson can sell $100,000 worth of goods, while a poor one can sell only $10,000 worth of goods. Job applicants know if they are good or bad, but the firm does not. A firm will offer job applicants a choice between a fixed salary of $2,000 or a commission on the sale. Assume risk-neutral salespersons and no opportunistic behavior. Given that the firm wants to distinguish a prospective
good salesperson from a poor one, what should be the commission on sales?
A) Commission should be larger than 50%.
B) Commission should be larger than 40%.
C) Commission should be between 2% and 20%.
D) Commission should be smaller than 2%.
C
You might also like to view...
The average output produced per worker is one way of measuring
A) inflation. B) the interest rate. C) employment. D) productivity.
When airplanes take off and land at Logan Airport, the residents of East Boston complain about the noise. The same planes make the same noise during the trip to Boston from Paris, but on this run, over the Atlantic
a. the sound is muffled at high altitudes, creating less market failure b. market failure does not apply because it is an international flight c. there are no externalities because there are no third parties d. the positive externalities of the flight outweigh the negative externalities of the noise e. free riders are more numerous so that market failure is eliminated
When looking at a graph of aggregate demand, which of the following is correct?
a. There are nominal variables on both the vertical and the horizontal axes. b. There are real variables on both the vertical and horizontal axes. c. The variable on the vertical axis is nominal; the variable on the horizontal axis is real d. The variable on the vertical axis is real; the variable on the horizontal axis is nominal
Refer to the information provided in Figure 28.6 below to answer the question(s) that follow.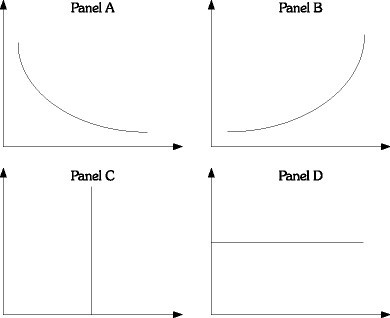 Figure 28.6Refer to Figure 28.6. Panel A represents the typical shape of the
Figure 28.6Refer to Figure 28.6. Panel A represents the typical shape of the
A. short-run Phillips curve. B. long-run Phillips curve. C. short-run aggregate supply curve. D. long-run aggregate supply curve.