Derive an equation for the net rate of radiant heat transfer from surface 1 in the system shown in the accompanying sketch. Assume that each surface is at a uniform temperature and that the geometrical shape factor F1–2 is 0.1.
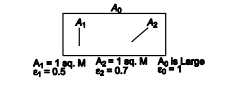
GIVEN
? The system shown above
FIND
? An expression for the net rate of radiant heat transfer from surface 1 (q1)
ASSUMPTIONS
? Steady state
? A1 and A2 are gray, A0 is black
? Each surface is at a uniform temperature
? The shape factor F12 = 0.1
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
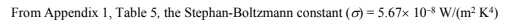
All of the shape factors for the problem can be expressed in terms of F12 using Equation (11.46) and the fact that all shape factors from a given surface must sum to unity. Also
The net rate of heat transfer from surface 1 is given by Equation (11.67)
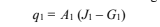
Where the radiosity (J1) and the irradiation (G1) can be calculated using Equations (11.69) and (11.66)
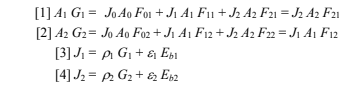
Substituting [4] into [1]
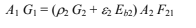
Substituting [2] and [3] into this Equation
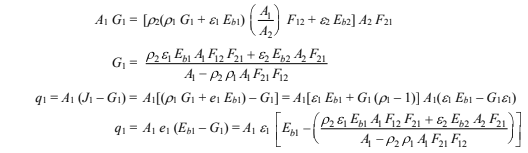
where
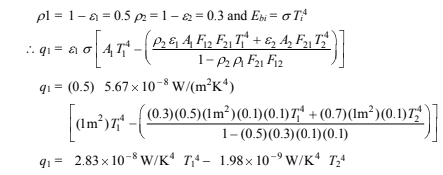
You might also like to view...
Light excites atomic hydrogen from its lowest level to the n = 4 level. What is the energy of the light? The energy of the lowest level is -13.6 eV
A) 12.8 eV B) 3.40 eV C) 0.850 eV D) 26.4 eV
When the microwave background radiation was emitted, about how big was the universe?
A) smaller than the head of a pin B) 1/1,000,000 its current size C) 1/100,000 its current size D) 1/1,000 its currents size E) 1/100 its current size
A steel ball bearing of mass m1 and speed of magnitude v1 has a head-on elastic collision with a steel ball bearing of mass m2 at rest. Rank the speed v1 of m1 relative to v2, the magnitude of the speed of m2, after the collision when i) m1>m2; ii) m1 = m2; and iii) m1
A. v1v2; v1>v2
Chemistry is the study of
A) matter. B) transformations of matter. C) only microscopic phenomena. D) only macroscopic phenomena. E) both A and B