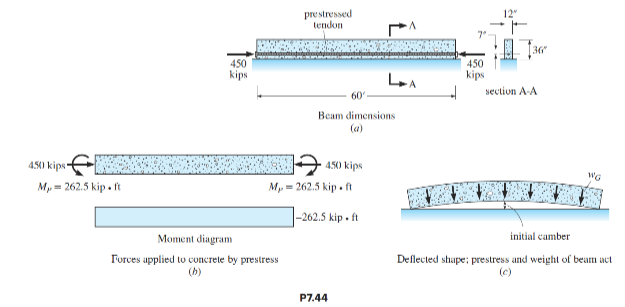
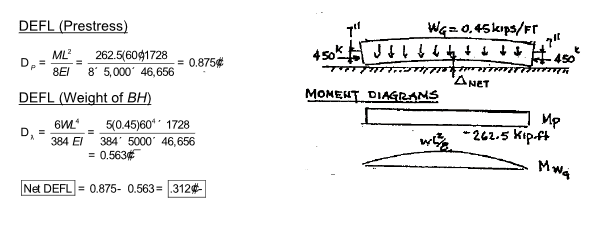
The reinforced concrete girder shown in Figure P7.44a is prestressed by a steel cable that induces a compression force of 450 kips with an eccentricity of 7 in. The external effect of the prestressing is to apply an axial force of 450 kips and equal end moment M P = 262.5 kip · ft at the ends of the girder (Figure P7.44b). The axial force causes the beam to shorten but produces no bending deflections. The end moments M P bend the beam upward (Figure P7.44c) so that the entire weight of the beam is supported at the ends, and the member acts as a simply supported beam. As the beam bends upward, the weight of the beam acts as a uniform load to produce downward deflection. Determine the initial camber of the beam at midspan immediately after the cable is tensioned. Note: Over time the
initial deflection will increase due to creep by a factor of approximately 100 to 200 percent. The deflection at midspan due to the two end moments equals ML 2 ?(8EI). Given: I = 46,656 in.4, A = 432 in. 2 , beam weight w G = 0.45 kip/ft, and E = 5000 kips/in. 2 .
You might also like to view...
KOEO stands for ____________________.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
The density of a gas that occupies 30 cubic feet and weighs 3 pounds is:
A) Density = 30 ft3/3 lb = 10 ft3/lb. B) Density = 3 lb/30 ft3 = 0.1 lb/ft 3. C) Density = 3 lb × 30 ft3 = 900 lb/ft3. D) Density = 30 ft3 + 3 lb = 33 lb/ft.3.
Define nesting blanks.
What will be an ideal response?
Which of the following influences cause a controlled variable to change?
A. a disturbance appears B. a load demand varies C. the set point is adjusted D. all of the above