Answer the following statement(s) true (T) or false (F)
1. The short run is any period of time less than one year, while the long run refers to a period of time one year or more in length.
2. The production function describes how much output a firm can generate for various cost levels.
3. Marginal and average products can be plotted in the same graph as total product costs.
4. In deriving the marginal product of labor, we consider the increase in output of an additional worker using additional capital.
5. In order to compute the total cost of production when labor is the only variable, we need only need to know the quantities of labor and the current wage rate.
1. False
2. False
3. False
4. False
5. False
You might also like to view...
Use the following graph to answer the next question.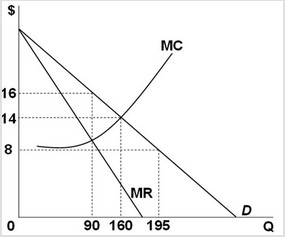 If the industry were a pure monopoly, the profit-maximizing price would be ________.
If the industry were a pure monopoly, the profit-maximizing price would be ________.
A. $8 B. $14 C. greater than $16 D. $16
The demand for loanable funds curve shows that the higher the real interest rate, the
A) more the loanable funds demand curve shifts leftward. B) smaller the demand for loanable funds. C) smaller the quantity of loanable funds demanded. D) larger the demand for loanable funds. E) larger the quantity of loanable funds demanded.
Scientists have said for years cod was so seriously overfished in European Union waters that there was a risk of extinction due to stock collapse
"To ensure this recovery… Ministers agreed a 10 percent cut in days at sea (for North Sea cod)," EU Fisheries Commissioner Joe Borg stated in 2008. What is the goal of this policy? A) To reduce the number of fishing days to the point where marginal cost per day equals marginal benefit B) To reduce the number of fishing days to the point where marginal social cost per day equals marginal benefit C) To reduce the number of fishing days to the point where marginal social benefit per day equals marginal benefit D) To reduce the number of fishing days to the point where marginal social cost per day equals marginal social benefit
Suppose the same basket of goods costs $200 in the U.S. and 100 pounds in Britain and that the exchange rate is $3 per pound. According to purchasing power parity, if the two countries' price levels do not change, what will happen to exchange rate?
a. The pound would appreciate until the exchange rate reaches $3 per pound. b. The pound would depreciate until the exchange rate reaches $2 per pound. c. The pound would depreciate until the exchange rate reaches $0.50 per pound. d. The dollar price of a pound would remain at $10. e. The pound would appreciate until the exchange rate reaches $4 per pound.