Indicate whether each of the following situations would shift the supply curve to the left, to the right, or not at all
a. An increase in the price of an input
b. An increase in productivity
c. An increase in the price of a substitute in production
d. A decrease in the expected future price of a product
e. A decrease in the current price of the product
a. Shift to the left
b. Shift to the right
c. Shift to the left
d. Shift to the right
e. No shift
You might also like to view...
The self-correcting tendency of the economy means that falling inflation eventually eliminates:
A. exogenous spending. B. recessionary gaps. C. expansionary gaps. D. unemployment.
A ration coupon limits how much a producer can produce
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Figure 4-13
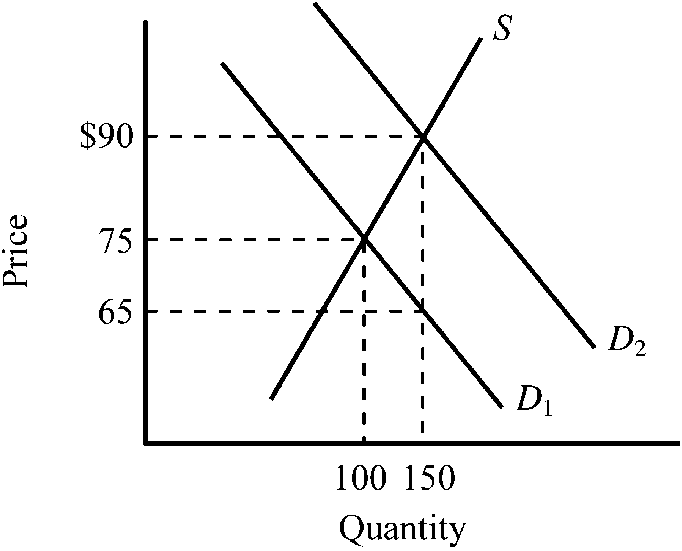
Refer to . The supply curve S and the demand curve D1 indicate initial conditions in the market for flu shots. A new government program is implemented that grants buyers a $25 subsidy when they buy a flu shot, shifting the demand curve from D1 to D2. Which of the following is true for this subsidy given the information provided in the figure?
a.
The original price of a flu shot was $75, and after the subsidy, it rises to $90.
b.
$65 represents the net price a buyer must pay for a flu shot after taking into account the subsidy payment.
c.
Buyers of flu shots will receive an actual benefit of $10 from the subsidy, while sellers of flu shots will receive an actual benefit of $15 from the subsidy.
d.
All of the above are true.
Suppose Kaylee withdraws $4,000 from her bank. If the reserve ratio is 25 percent, then this will lead to a decrease in M1 of:
A. $1,000. B. $4,000. C. $8,000. D. $12,000.