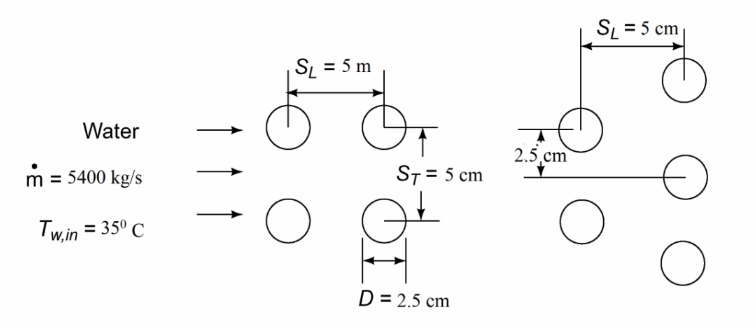
Compare the rate of heat transfer and the pressure drop for an in-line and a staggered arrangement of a tube bank consisting of 300 tubes, 1.8 m long and 2.5 cm OD. The tubes are to be arranged in 15 rows with longitudinal and transverse spacing of 5 cm. The tube surface temperature is 95°C and water at 35°C is flowing at a mass rate of 5400 kg/s over the tubes.
GIVEN
Water flowing over an in-line and a staggered tube bank
Number of tubes (Nt) = 300
Length of tubes (L) = 1.8 m
Tube outside diameter (D) = 2.5 cm= 0.025 m
Number of rows (N) = 15
Normal and parallel spacing = 5 cm=0.05 m
Tube surface temperature (Tt) = 95°C
Water inlet temperature (Tw,in) = 35°C
Mass flow rate of water (m) = 5400 kg/s
FIND
(a) Compare the rate of heat transfer (q) and
(b) The pressure drop ( ?p) for the two configurations
ASSUMPTIONS
Steady state
Tube temperature is uniform
SKETCH
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for water at the inlet temperature of 35°C
Density (?) = 994.1 kg/m3
Thermal conductivity (k) = 0.624 W/(m K)
Prandtl number (Pr) = 4.8
Specific heat (c) = 4175 J/(kg K)
At the tube temperature of 95°C
Prs = 1.88
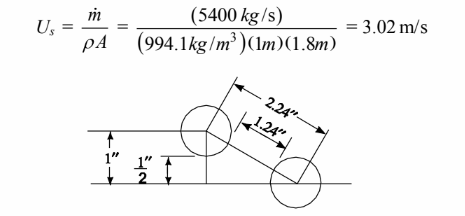
The water velocity can be calculated with the help of the sketch below.
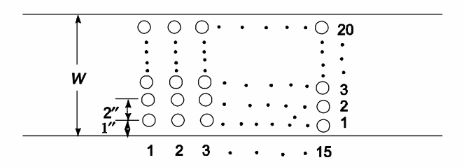
W = 19(5 cm) + 5 cm = 100 cm = 1 m
Therefore, the water velocity is
Therefore, for the staggered configuration, the minimum free area is between adjacent tubes in a row,
and the maximum air velocity is
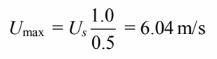
This is also the maximum velocity for the in-line case.
The Reynolds number for either case is

(a) The Nusselt number for the in-line case is given by
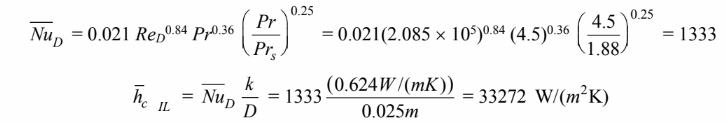
The Nusselt number for the staggered case is given by

These heat transfer coefficient differ by only 5%, therefore, the rate of heat transfer for the two tube
banks will be nearly equal.
(b) These pressure drop is given by
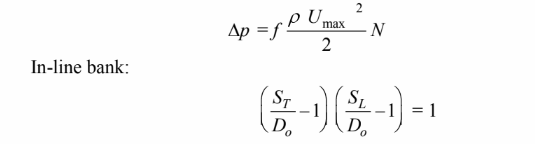
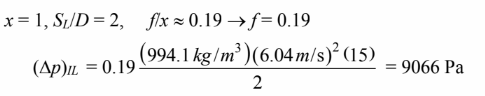
Staggered tube bank:
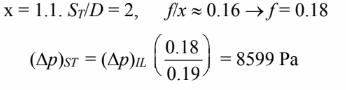
For nearly the same rate of heat transfer, the staggered bank has slightly lower pressure drop.
COMMENTS
These results are only true because the flow is turbulent. Greater difference would occur at lower
Reynolds numbers.
You might also like to view...
Spaceman Speff orbits spherical asteroid X with his spaceship. To remain in a circular orbit at 421 km from the asteroid's center, he should maintain a speed of What is the mass of planet X? (G = 6.67 × 10-11 N ? m2/kg2)
A) 4.0 × 1019 kg B) 5.1 × 1017 kg C) 4.0 × 1016 kg D) 5.1 × 1014 kg
While more massive than most of its neighbors, our Sun is still technically a low-mass star
Indicate whether the statement is true or false
The ratio of mass to volume is known as ______________
Fill in the blank(s) with correct word
In the lab, charged particles are directed toward one another, each at speed 0.500 c. What is the speed of the particles moving toward the left with respect to the particles moving to the right?
A. 0.500 c B. 0.00 C. 1.00 c D. 0.800 c E. 1.25 c