Light with a wavelength of 310 nm is incident on a metal that has a work function of 3.80 eV. What is the maximum kinetic energy that a photoelectron ejected in this process can have?
(1 eV = 1.60 × 10-19 J, c = 3.00 × 108 m/s, h = 6.626 × 10-34 J ? s)
A) 0.62 × 10-19 J
B) 0.21 × 10-19 J
C) 0.36 × 10-19 J
D) 0.48 × 10-19 J
E) 0.33 × 10-19 J
E
You might also like to view...
Identify the FALSE statement:
A fifth-generation star would have a greater proportion of heavier elements than a second-generation star. The elements of any person's body were once star matter; therefore we are all literally made of stardust. Our Universe is so old there are no first-generation stars left in it. Dense regions of a nebula pull in surrounding material and therefore grow in mass and density and rotate faster. An accretionary disk eventually grows hot and massive enough to become a protostar, then a star.
A constant electric field 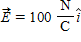
A. 0. B. 0.25. C. 25. D. 50. E. 100.
A certain automobile engine takes in 4.00 kJ of energy and performs 1.10 kJ of mechanical work in each cycle. (a) Calculate the engine's efficiency. (b) How much thermal energy is "wasted" in each cycle?
What will be an ideal response?
An object with a nonzero rest mass moving at the speed of light would have
A. time pass at an infinitely fast rate. B. infinite apparent mass. C. no momentum. D. infinite volume.