Under fixed exchange rates, a central bank
a. adjusts the money supply automatically and immediately to changes in the demand and supply of foreign exchange
b. need hold no reserves of foreign exchange
c. enforces the fixed exchange rate by refusing to buy or sell foreign exchange whenever changes occur in demand or supply
d. may find its reserves fluctuating as demand and supply conditions change
e. has no authority to buy or sell foreign exchange
D
You might also like to view...
Potential GDP increased from 4.7 trillion to 16.6 trillion between 1970 and 2013 resulting in economic growth. Also, during this time ________ occurred because ________
A) inflation; aggregate demand decreased by more than potential GDP B) stagflation; aggregate demand increased by more than potential GDP C) deflation; aggregate demand increased by more than potential GDP D) inflation; aggregate demand increased by more than potential GDP E) inflation; aggregate demand increased by less than potential GDP
Government policies to raise the rate of productivity growth include all of the following except
A) improving infrastructure. B) improving forecasts of unemployment. C) helping build human capital by worker training programs. D) encouraging research and development.
Dumping is considered a practice that seriously harms domestic producers because
A) the quality of the dumped good is superior to that of the importing country. B) it allows the exporting country to use poor quality materials. C) it establishes a price that cannot be met by domestic producers. D) it discriminates between wealthy and poor countries.
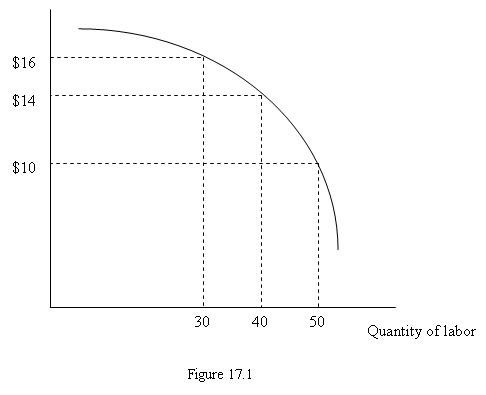 Figure 17.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the prevailing hourly wage decreases:
Figure 17.1 depicts a firm's marginal revenue product curve. If the prevailing hourly wage decreases:
A. the marginal revenue product curve shifts upward. B. the marginal revenue product curve shifts downward. C. the marginal revenue product curve does not shift, but there is a movement upward along the curve. D. the marginal revenue product curve does not shift, but there is a movement downward along the curve.