Indicate the order of the point mutations in the rII region.
Shown below are the maps of a series of rII- deletion strains (1–5). The deleted region is indicated as (......) and the intact region as ______.
1 ___________(...........)_______________
2 _________________(...........)_________
3 (.....................)_____________________
4 ________________________(................)
5 _____(..........)______________________
rII- phage strains A-E have point mutations in the rII region. E.coli K(?) cells are coinfected with one phage that has a deletion and one phage that has a point mutation. The presence of wild-type progeny phage is assessed by the presence (+) or absence (o) of plaques.
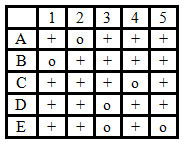
A) CADBE
B) DEBAC
C) BADCE
D) ABDEC
E) CEADB
B) DEBAC
You might also like to view...
The pancreas is an organ that regulates blood glucose levels. When glucose levels rise above normal, the pancreas
releases insulin to lower blood glucose levels. This is an example of ____. a. evolution b. mutation c. immunity d. homeostasis e. variability
What is the most common element in your body?
A) Oxygen B) Water C) Carbon D) Sugar
The letter designation of human blood type is controlled by a single gene with three alleles (the allele that produces type A blood, the allele that produces type B blood, and the allele that produces type O blood). This is an example of _______.
a) incomplete dominance b) a polygenic trait c) environmental influence d) multiple allele inheritance
What is the site of fetal metabolic waste processing?
A. Fetal Liver & Kidneys B. Fetal Spleen C. Maternal Liver & Kidneys D. Maternal Spleen E. Placenta