In Figure 5.1, what profit would a perfect competitor earn? 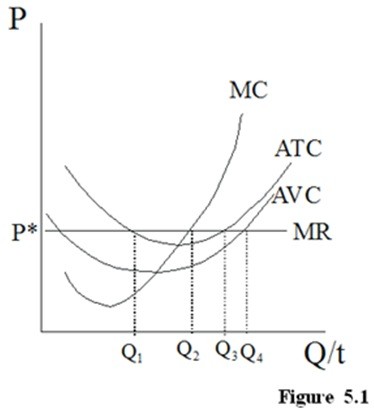
A. a loss greater than its total fixed cost
B. a loss less than its total fixed cost
C. a profit of zero
D. a positive profit
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
The aggregate demand curve for an economy depicts the:
a. quantity of goods and services demanded during a given time period at different interest rates, other things held constant. b. quantity of goods and services demanded at different price levels during different time periods, other things held constant. c. quantity of goods and services demanded at different price levels during a given time period, other things held constant. d. quantity of goods and services that the economy is capable of producing during a given time period, other things held constant. e. final quantity of goods and services actually produced by the economy during a given time period, other things held constant.
The EITC tends to
a. increase employment just like the minimum wage does. b. decrease employment just like the minimum wage does. c. increase employment whereas the minimum wage decreases employment. d. decrease employment whereas the minimum wage increase employment.
The television network newscaster reports that the national inflation rate in the past year was equal to 4 percent. This report is most likely prepared from work done by a(n)
a. microeconomist b. normative economist c. macroeconomist d. econometrician e. social scientist rather than an economist
As long as a market is contestable, then even if it has only a few sellers, the
a. threat of new entrants will prevent the prices from rising above the competitive level. b. producers will be able to charge prices that are high enough to produce long-run economic profits. c. producers will not face new competition because the barriers to entry are high. d. market will never be expected to come close to the competitive result.