Suppose the Canadian government agrees to establish an official exchange rate at which 1$ Canadian is equal to $0.925 U.S. Now suppose the demand for the Canadian dollar increases as more Americans travel to Canada causing the demand curve for Canadians dollars to shift to the right as shown in Figure (a). If the Canadian government wishes to maintain the official exchange rate then it must increase the supply of its currency as shown in Figure (b) by
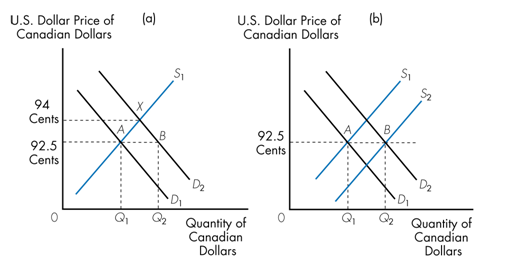
a. selling U.S. dollars.
b. buying U.S. dollars.
c. restrict the amount of Canadian dollars in foreign exchange markets.
d. Any of the above.
b. buying U.S. dollars.
You might also like to view...
Whenever you discount a future sum of money into its present value, you must know I. the interest rate. II. the number of years in the future in which the money will be received
A) only I B) only II C) both I and II D) neither I nor II
If the cost were greater than the marginal benefit of a good:
A. consumers could increase their utility by buying more. B. consumers could increase their utility by buying less. C. producers should increase production. D. social net benefit would be maximized.
If prices are free to rise and fall, and supply and demand cross at a positive price, quantity combination, neither excess demand nor excess supply can persist in a market
a. True b. False
Which of the following is not a requirement for the existence of monopolistic competition in a market?
a. numerous small sellers b. full information about the market among buyers and sellers c. product homogeneity d. freedom of entry into the market