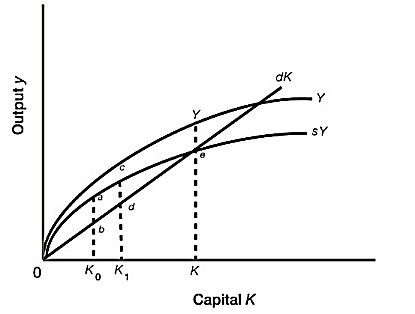
 Refer to Figure 13A.1. Moving from K0 to K1:
Refer to Figure 13A.1. Moving from K0 to K1:
A. economic growth stops.
B. saving becomes negative.
C. capital stock continues to increase.
D. depreciation starts to decline.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
The law of demand is graphically demonstrated by a(n):
a. perfectly vertical demand curve. b. perfectly horizontal demand curve. c. downward-sloping demand curve. d. upward-sloping demand curve. e. curved demand line.
Jake just quit his job as a shoe salesman and is looking for work as an accountant, which is what his college degree is in. Jake would be considered:
A. frictionally unemployed. B. structurally unemployed C. cyclically unemployed. D. Jake is not in the labor force.
The long-run price elasticity of demand for a good is
a. zero b. smaller (in absolute value) than the short-run price elasticity c. larger (in absolute value) than the short-run price elasticity d. infinite e. the same as the short-run elasticity
Joseph Schumpeter's explanation of why economies experience business cycles focuses on
a. the climatic cycles caused by movements in the solar system b. the impact of war activity on the economy c. housing construction d. the clustering of innovations e. the interaction of the multiplier and the accelerator