South Korea, Indonesia, Malaysia, and Thailand all pegged their currencies to the dollar at one point in time
Because some of these currencies were overvalued at the pegged rate, speculators anticipated these countries would abandon the peg and speculators began selling those currencies. Explain how this speculation would affect the ability of a country to maintain a pegged exchange rate.
As speculators began selling currencies that were pegged to the dollar, this increased the supply of those currencies and increased the demand for the dollar. The result was downward pressure on the prices of currencies pegged to the dollar. However, because these currencies were pegged, the central banks of these countries had to purchase the surplus currency being sold in the foreign exchange markets. To continue purchasing the surplus currency, these countries needed foreign currency (mostly dollars). As reserves of dollars began to fall, it became more difficult for these countries to maintain the peg.
You might also like to view...
Which of the following is not a property of a competitive equilibrium?
A) markets clear. B) consumers and firms optimize given market prices. C) the government budget constraint is satisfied. D) increasing total factor productivity.
You notice that the price of orange juice at your local grocery store has increased. Which of the following statements is not a possible explanation for the rise in the price of orange juice? a. Frosty weather destroys oranges causing the price of oranges to increase
b. As a result of an increase in income, consumers wish to purchase more orange juice at every price level. c. A recent scientific study is reported in the press that suggests that apple juice may be contaminated with pesticides. d. Due to the bioengineering of orange trees, the domestic supply of oranges increases.
Figure 10-9
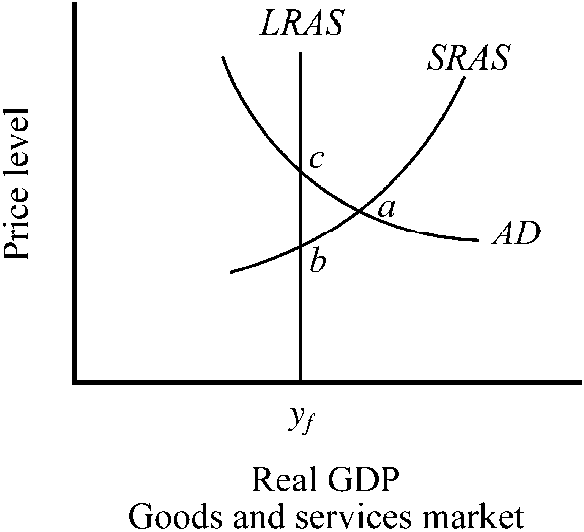
The output of the economy depicted in is
a.
equal to the full-employment output level.
b.
less than the full-employment output level.
c.
greater than the full-employment output level.
d.
sustainable in the long run.
Suppose an economy exhibits general conditions of downward-sloping labor demand, upward-sloping supplies of domestic and immigrant labor, and a competitive labor market. Which of the following is not a likely outcome of immigration?
A. Some economic surplus will transfer from domestic workers to domestic firms. B. Domestic workers who keep their job will experience an increase in earnings. C. Economic surplus will increase in the destination country, even net of immigrant earnings. D. Domestic workers will experience some job losses. E. The market-clearing wage will fall.