Efficiency wages, minimum-wage laws, and unions all keep wages
a. below the equilibrium level, causing a shortage of labor.
b. below the equilibrium level, causing a surplus of labor.
c. above the equilibrium level, causing a shortage of labor.
d. above the equilibrium level, causing a surplus of labor.
d
You might also like to view...
To answer the next question, use the following graph showing the domestic demand and supply curves for a specific standardized product in a particular nation.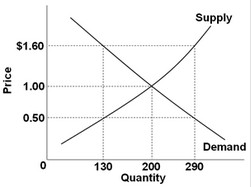 If the world price for this product is $0.50, this nation will experience a domestic
If the world price for this product is $0.50, this nation will experience a domestic
A. shortage of 160 units, which it will meet with 160 units of imports. B. surplus of 160 units, which it will export. C. shortage of 160 units, which will increase the domestic price to $1.60. D. surplus of 160 units, which will reduce the world price to $1.00.
Use the following graphs to answer the next question. In the graphs, the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The economy is at point Y on the investment demand curve. Given these conditions, what policy should the Fed pursue to achieve a noninflationary, full-employment level of real GDP?
In the graphs, the numbers in parentheses near the AD1, AD2, and AD3 labels indicate the level of investment spending associated with each curve. All figures are in billions. The economy is at point Y on the investment demand curve. Given these conditions, what policy should the Fed pursue to achieve a noninflationary, full-employment level of real GDP?
A. Increase aggregate demand from AD3 to AD2. B. Increase interest rates from 4% to 8%. C. Decrease the money supply from $225 billion to $150 billion. D. Make no change in monetary policy.
Refer to the accompanying figure. At point D, the opportunity cost of making milk is: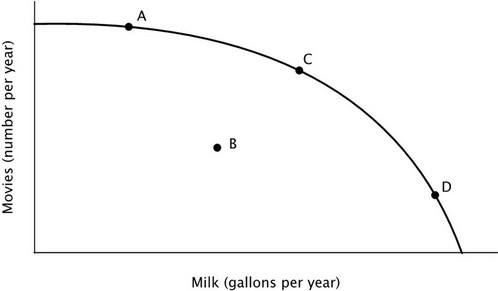
A. high because productive resources that are better-suited to making movies are being used to make milk. B. low because the economy is specializing in making milk. C. high because productive resources that are better-suited to making movies are not being used to make milk. D. high because the economy is not operating efficiently.
A primary emphasis of the Keynesian school is the economy has a tendency to:
A. always create a full-employment level of output. B. always create inflationary pressure at all levels of output. C. eliminate unemployment by lowering wage rates to create an equilibrium in the labor market. D. be in equilibrium at less than full employment.