When will a wage increase cause a firm to produce more output in the long run?
a. Always.
b. When labor and capital are complements in production.
c. When labor is a regressive factor.
d. Never.
c. When labor is a regressive factor.
You might also like to view...
U.S. Gross Domestic Product (GDP) does NOT include which of the following?
A) the value of goods produced in a foreign country by U.S. owned firms B) the purchase of all final goods and services by U.S. households C) U.S. exports to other countries D) business investment in the United States
Which of the following factors is associated with products with a highly price elastic demand?
a. Few close substitutes. b. A very short time period for consumers to respond to price changes. c. Many very close substitutes. d. A per unit price that is only a very small portion of most peoples' budgets.
Refer to the information provided in Figure 7.10 below to answer the question(s) that follow. 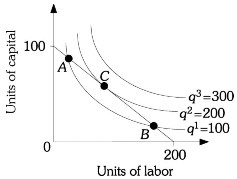 Figure 7.10Refer to Figure 7.10. At Point C, the slope of q2 = 200 is
Figure 7.10Refer to Figure 7.10. At Point C, the slope of q2 = 200 is
A. -2. B. -1/2. C. -1. D. indeterminate from this information.
What roles do human capital and compensating differentials play in shaping the wage that a firm will pay a new employee?
What will be an ideal response?