Which of the following characterizes parthenogenesis?
A) An individual may change its sex during its lifetime
B) Specialized groups of cells grow into new individuals
C) An organism is first a male and then a female
D) An egg develops without being fertilized
E) Both mates have male and female reproductive organs
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Which of the following cells are diploid?
a. sperm b. primary spermatocytes c. secondary spermatocytes d. male germ cells e. both primary spermatocytes and male germ cells
A constitutive mutation in the lac operon may be of several types. Name two types of constitutive mutations
What will be an ideal response?
Your family is taking a long driving vacation across the midwestern and western United States. As you travel, you notice that the flowers, birds, and trees of the Midwest and the Rocky Mountains are very different. As you ponder why, you remember that such differences in the distribution of species are part of the field of ______.
a. biogeography b. geology c. morphology d. paleontology
The Earth is spherical, which causes differences in the intensity of solar radiation at different latitudes. The Earth is also titled on its axis at a 23.5° angle. How do you think this tilt affects the intensity of solar radiation?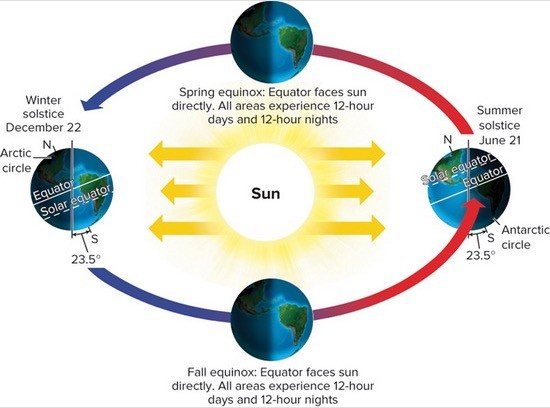
A. The Northern hemisphere has a higher intensity of solar radiation than the Southern hemisphere because it is tilted toward the Sun year round. B. The sun's rays strike the Northern hemisphere more obliquely during its winter months and less obliquely during its summer months. C. The Northern hemisphere has a lower intensity of solar radiation than the Southern hemisphere because it is tilted away from the Sun year round. D. The sun's rays strike the Northern hemisphere more obliquely during its summer months and less obliquely during its winter months. E. In the Northern and Southern hemispheres, equal latitudes receive the sun's rays at equal angles year round.