For the first 1 billion years of Earth's evolution, the fraction of oxygen in its atmosphere was approximately
a. zero.
b. half of what it is today.
c. 2 times what it is today.
d. 10 times what it is today.
e. the same as it is today.
a. zero.
You might also like to view...
A firecracker breaks up into two pieces, one has a mass of 200 g and flies off along the x-axis with a speed of 82.0 m/s and the second has a mass of 300 g and flies off along the y-axis with a speed of 45.0 m/s
What is the total momentum of the two pieces? A) 361 kg?m/s at 56.3° from the x-axis B) 93.5 kg?m/s at 28.8° from the x-axis C) 21.2 kg?m/s at 39.5° from the x-axis D) 361 kg?m/s at 0.983° from the x-axis E) 21.2 kg?m/s at 56.3° from the x-axis
A Trombe wall is a masonry wall often used in passive solar homes to store solar energy. Suppose that such a wall, fabricated from 20-cm-thick solid concrete blocks (k = 0.13 W/(mK), ? = 0.05 × 10–5 m2/s) is initially at 15°C in equilibrium with the room in which it is located. It is suddenly exposed to sunlight and absorbs 500 W/m2 on the exposed face. The exposed face loses heat by radiation and convection to the outside ambient temperature of –15°C through a combined heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/(m2 K). The other face of the wall is exposed to the room air through a heat transfer coefficient of 10 W/(m2 K). Assuming that the room air temperature does not change, determine the maximum temperature in the wall after 4 hours of exposure and the net heat transferred to the room.
GIVEN • Trombe wall suddenly exposed to sunlight FIND (a) Maximum temperature in the wall after 4 hours (b) Heat input to the room
A 0.330-kg volleyball is thrown vertically downward with a speed of 0.150 m/s in a place where g = 9.81 m/s2. It takes it 0.0655 s to reach the ground. What is the magnitude of its momentum just before it hits the ground?
A) 0.212 kg ? m/s B) 0.262 kg ? m/s C) 0.163 kg ? m/s D) 0.0216 kg ? m/s E) 0.0418 kg ? m/s
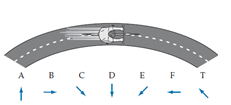
A bike (shown in a top view in the diagram) travels around a curve with its brakes on, so that it is constantly slowing down. Which of the arrows shown most closely approximates the direction of the bike’s acceleration at the instant it is at the position shown? (Hint: Draw a motion diagram.)
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
E. E
F. F
T. T