When a ferromagnetic material that has been magnetized is brought to a temperature greater than the Curie temperature, what happens to its residual magnetism
a. Nothing happens to the residual magnetism.
b. The residual magnetism disappears.
c. The residual magnetism reaches it's highest value. d. All the magnetic domains causing magnetism become a single domain.
e. The material of the magnet melts causing currents that are magnetic.
B
You might also like to view...
The energy absorbed as heat by an ideal gas for an isothermal process equals:
A. the work done by the gas B. the work done on the gas C. the change in the internal energy of the gas D. the negative of the change in internal energy of the gas E. zero since the process is isothermal
Two satellites are placed in geosynchronous orbits, orbits with a period of 24 hours, where each satellite hovers over a spot on the Earth's equator. Satellite B has three times the mass of satellite A. What is the relationship between the magnitudes of the gravitational forces of the Earth on the two satellites?
A.
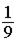 FA.
FA.B.
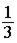 FA.
FA.C.
D.
E.
Two 2-m/s pool balls roll toward each other and collide. Suppose after bouncing apart each moves at 4 m/s. This collision violates the conservation of
A) momentum. B) energy. C) both momentum and energy. D) none of the above
Which statement concerning black hole masses and Schwarzschild radii is not true?
A) In a binary system with a black hole, the Schwarzschild radius depends on the distance from the black hole to the companion star. B) For black holes produced in massive star supernovae, Schwarzschild radii are typically a few to a few tens of kilometers. C) The more massive the black hole, the larger the Schwarzschild radius. D) Even an object as small as you could become a black hole if there were some way to compress you to a size smaller than your Schwarzschild radius.