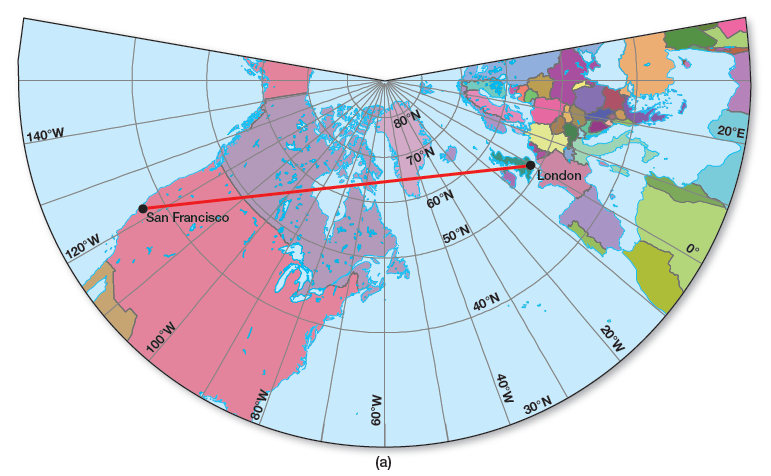
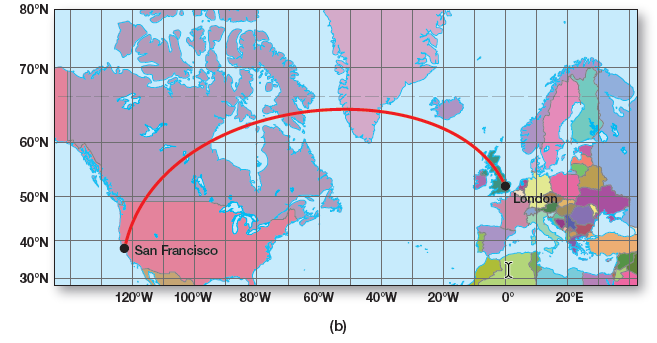
Use the two maps in Figure 4.5 to plot a great circle route between San Francisco (west coast of the United States, where you can see small details of San Francisco Bay) and London (southern England at the 0° prime meridian). The straight line on the gnomonic projection will show the shortest route between the two cities. Transfer the coordinates of this route over to the Mercator map and connect with a line plot to show the route’s track. Note the route arching over southern Greenland on the Mercator.
What will be an ideal response?
Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences
You might also like to view...
A hundred years ago, how did farmers develop new varieties of squash to resist the squash borer insect pest?
A. crossbreeding B. genetic engineering C. natural selection D. artificial insemination
Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences
What mechanisms might explain the warm climate of the Mesozoic Era? How might the equator-to-pole temperature gradient have been reduced?
What will be an ideal response?
Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences
The term cooling degree day is used during ____ weather
a. warm b. cold c. freezing d. humid e. any
Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences
How large is a typical, single air mass?
A. The size of a continent (e.g., North America) B. The size of a larger state (e.g., Wyoming) C. The size of a region (e.g., eastern United States) D. The size of a small state (e.g., Delaware)
Environmental & Atmospheric Sciences