A plane is moving due north, directly towards its destination. Its airspeed is 210 mph. A constant breeze is blowing from west to east at 25.0 mph. In which direction is the plane pointed?
a. 6.79° W of N
b. 83.2° W of N
c. 44.8° W of N
d. 83.2° E of N
e. 45.2° E of N
a
You might also like to view...
Total Internal Reflection: A point source of light is positioned 20.0 m below the surface of a lake. What is the diameter of the largest circle on the surface of the water through which light can emerge into the air? The index of refraction of water is 1.33.
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
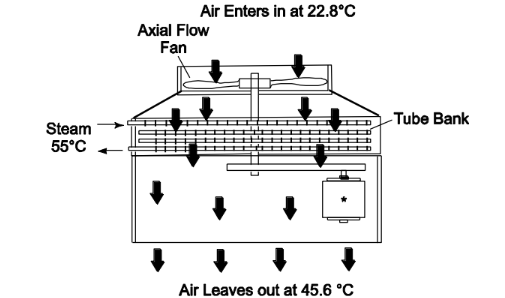
An air-cooled low-pressure-steam condenser is shown in following figure.
The tube bank is four rows deep in the direction of air flow and there are total of 80 tubes. The tubes have ID = 2.2 cm and OD 2.5 cm and are 9-m-long with circular fins on the outside. The tube-plus-fin area is 16 times the bare tube area (i.e., the fin area is 15 times the bare tube area, neglect the tube surface covered by fins). The fin efficiency is 0.75. Air flows past the outside of the tubes. On a particular day, the air enters at 22.8°C and leaves at 45.6°C. The air flow rate is 3.4 × 105 kg/h. The steam temperature is 55°C and has a condensing coefficient of 104 W/(m2 K). The steam-side fouling coefficient is 104 W/(m2K). The tube wall conductance per unit area is 105 W/(m2K). The air-side fouling resistance is negligible. The air-side-film heat transfer coefficient is 285 W/(m2K). (Note this value has been corrected for the number of transverse tube rows.) (a) What is the log-mean temperature difference between the two streams? (b) What is the rate of heat transfer? (c) What is the rate of steam condensation? (d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins.
GIVEN
• The condenser shown above
• Number of tubes (N) = 80 and number of rows (Nr) = 4 (in air flow direction)
• Tube diameters Di = 2.2 cm = 0.022 m Do = 2.5 cm = 0.025 m
• Tube length (L) = 9 m
• Air temperature Ta,in = 22.8°C Ta,out = 45.6°C
• Air flow rate m a= 3.4 × 105 kg/h = 94.4 kg/s
• Steam temperature = 55°C (constant)
• Fin area = 15 (tube area)
• Fin efficiency (?f) = 0.75
• Steam side
Transfer coefficient h i= 104 W/(m2 K)
Fouling coefficient (1/Ri) = 104 W/(m2 K)
• Tube wall conductance per unit area (1/Rk) = 105 W/(m2 K)
• Air side: Transfer coefficient h o= 285 W/(m2 K)
• Fouling resistance on the air side is negligible
FIND
(a) The log-mean temperature difference(LMTD)
(b) The rate of heat transfer (q)
(c) The rate of steam condensation m
(d) Estimate the rate of steam condensation if there were no fins 2cm
ASSUMPTIONS
• Air side transfer coefficient is the same with or without fins
• Tube surface covered by the fins is negligible
PROPERTIES AND CONSTANTS
for dry air at the average temperature of 34.2°C,
the specific heat (cpa) = 1013 J/(kg K),
for steam at a saturation temperature of 55°C,
the heat of vaporization (hfg) = 2600 (kJ/kg)
A 50-cm3 block of wood is floating partially submerged in water, and a 50-cm3 block of iron is totally submerged in water. Which block has the greater buoyant force on it?
A) the wood B) the iron C) Both have the same buoyant force. D) The answer cannot be determined without knowing the densities of the blocks.
The rate of seafloor spreading can be calculated by
A) the magnetic pattern generated at the ocean floor. B) knowing the dates for magnetic pole reversals, and the distance from the location of a known reversal site to the ocean ridge. C) looking at the magnetic tape recording of the ocean floor. D) the rate of seafloor spreading cannot be calculated.