Find A, B, and C for the partial fraction decomposition.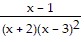 =
= 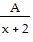 +
+ 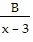 +
+ 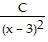
A. A = -  , B = -
, B = - 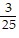 , C =
, C = 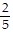
B. A =  , B =
, B = 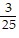 , C =
, C = 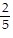
C. A = - 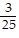 , B =
, B =  , C =
, C = 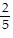
D. A =  , B = -
, B = - 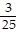 , C =
, C = 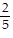
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Provide an appropriate response. Use only the numbers 2, 5, 8, and 9. Fill in the blanks to yield the smallest whole number: ___ - ___ + ___ × ___ = ?
A. 8 ? 5 + 2 × 9 = ? B. 9 ? 8 + 2 × 5 = ? C. 5 ? 2 + 9 × 8 = ? D. 9 ? 5 + 2 × 8 = ?
Solve the problem. Round your answer, if appropriate.Boyle's law states that if the temperature of a gas remains constant, then PV = c, where  ,
, 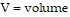 , and c is a constant. Given a quantity of gas at constant temperature, if V is decreasing at a rate of 10 in. 3/sec, at what rate is P increasing when P = 20 lb/in.2 and V = 70 in.3? (Do not round your answer.)
, and c is a constant. Given a quantity of gas at constant temperature, if V is decreasing at a rate of 10 in. 3/sec, at what rate is P increasing when P = 20 lb/in.2 and V = 70 in.3? (Do not round your answer.)
A.  lb/in.2 per sec
lb/in.2 per sec
B.  lb/in.2 per sec
lb/in.2 per sec
C. 140 lb/in.2 per sec
D. 35 lb/in.2 per sec
Use the sequence feature of a graphing calculator to evaluate the sum of the first 10 terms of the arithmetic sequence. Round to the nearest thousandth, if necessary.an =  n +
n + 
A. 166.633 B. 117.944 C. 140.304 D. 116.212
Find all absorbing states for the transition matrix, and indicate whether or not the matrix is that of an absorbing Markov chain.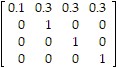
A. States 2, 3, and 4 are absorbing; the matrix is that of an absorbing Markov chain. B. States 2, 3, and 4 are absorbing; the matrix is not that of an absorbing Markov chain. C. States 3 and 4 are absorbing; the matrix is that of an absorbing Markov chain. D. States 2 and 3 are absorbing; the matrix is that of an absorbing Markov chain.