What was the Cambrian explosion?
A) the impact of the meteor that led to mass extinction of the dinosaurs
B) the initial spark of lightning that created the first life-form from amino acids
C) the eruption of the volcano known as Cambria on the ancient supercontinent of Pangaea
D) a dramatic diversification of life that began about 540 million years ago
E) the largest mass extinction in Earth's history
D
You might also like to view...
A uniaxial carbon-fiber reinforced composite material is subject to an axial tensile stress. It is desired to determine the actual stress in the graphite fibers using x-ray diffraction, because the calculation of stress equal to force divided by the area of the composite is not valid for the graphite fibers. Graphite fibers have a hexagonal structure, with the basal plane oriented parallel to the fiber axis and the c axis perpendicular to the fiber axis. In the graphite unit cell, there are two sets of parallel graphite planes, with a c lattice parameter of 0.6708 nm. The spacing between individual graphite planes is 0.3354 nm. With x-ray diffraction it is observed that the (0002) peak from the graphite fibers using chromium K? x-rays of wavelength 0.2291 nm is at an angle 2? of 39.98
degrees. The in plane elastic modulus of the graphite fibers is 400 GPa and Poisson’s ratio is 0.20. (a) What is the strain in the graphite fibers perpendicular to the fiber axis? (b) What is the strain in the graphite fibers parallel to the fiber axis? (c) What is the tensile axial stress in the graphite fibers?
Equilibrium: A 10-kg sign is held by two ropes as shown in the figure. What is the tension on rope A?
A. 44 N B. 69 N C. 72 N D. 88 N E. 98 N
An object starts from rest with an acceleration of 2.0 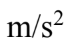 for 3.0 seconds. It then reduces its acceleration to 1.0
for 3.0 seconds. It then reduces its acceleration to 1.0 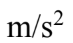 for 5.0 additional seconds. The total distance covered is
for 5.0 additional seconds. The total distance covered is
A. 52 m. B. 38 m. C. 11 m. D. 9.0 m. E. 7.6 m.
A camera has a lens that has an adjustable film distance used for focusing purposes. When the object being photographed is at a very large distance, the distance from the lens to the film is 50.0 mm. What would be the lens-to-film distance for an in-focus object 2.00 m from the camera?
a. 66.7 mm c. 51.3 mm b. 40.0 mm d. 48.8 mm