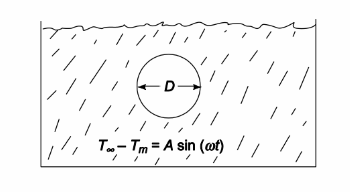
A small aluminum sphere of diameter D, initially at a uniform temperature To, is immersed in a liquid whose temperature, T?, varies sinusoidally according to
T? – Tm = A sin (? t) where: Tm = time-averaged temperature of the liquid A = amplitude of the temperature fluctuation ? = frequency of the fluctuations
If the heat transfer coefficient between the fluid in the sphere, ah , is constant and the system may be treated as ‘lumped capacity,’ derive an expression for the sphere temperature as a function of time.
GIVEN
• A small aluminum sphere is immersed in a liquid whose temperature varies sinusoidally
• Diameter of sphere = D
• Liquid temperature variation: T? – Tm = A sin (? t)
• The heat transfer coefficient = ah (constant)
• The system may be treated as a ‘lumped capacity’
FIND
• An expression for the sphere temperature as a function of time
ASSUMPTIONS
• Constant thermal conductivity
SKETCH
Let k = thermal conductivity of sphere
? = density of sphere c = specific heat of sphere An energy balance on the sphere yields
Change in internal energy = heat transfer to liquid
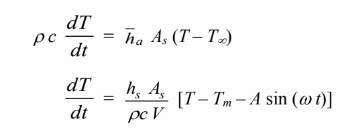
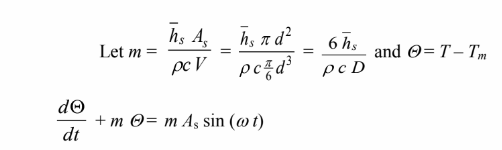
This is a first order, linear, non-homogeneous differential equation. The general solution is the sum of the homogeneous solution and a particular solution. The homogeneous solution is determined by the characteristic equation, found by substituting ? = e?t into the homogeneous equation
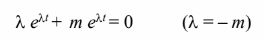
The homogeneous solution is ?h = Ce–mt. As a particular solution, try ?p = K cos (? t) + M sin (? t), substituting ?p and its derivative into the energy balance
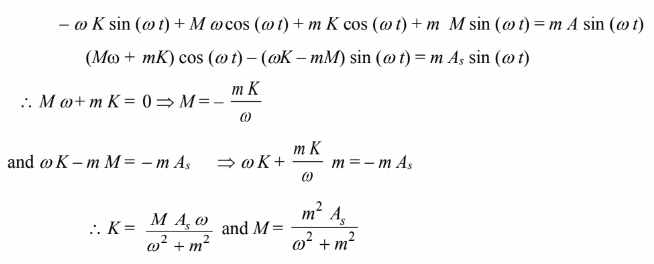
Therefore, the general solution is
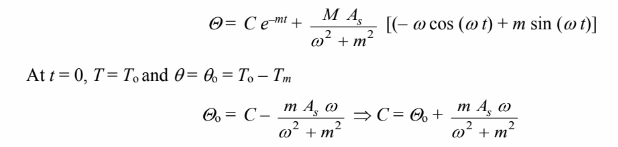
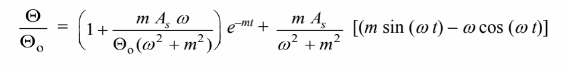
You might also like to view...
What do we mean by "life as we know it"?
What will be an ideal response?
If the temperature of a wire increases, its resistance
a. increases. b. decreases. c. does not change. d. will increase or decrease depending on the composition. e. will change in a way that can not be determined.
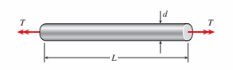
A brass rod of length L 5 0.75 m is twisted by torques T until the angle of rotation between the ends of the rod is 3.58. The allowable shear strain in the copper is 0.0005 rad. The maximum permissible diameter of the rod is approximately:
(A) 6.5 mm
(B) 8.6 mm
(C) 9.7 mm
(D) 12.3 mm
Gravitational lensing
a. occurs when light passes near a massive object and is deflected by the object's gravitational field. b. can be used to determine the luminosity of a galaxy. c. occurs when the mass of a galaxy is greater than expected from the luminosity of the galaxy. d. occurs when the mass of a galaxy is less than expected from the luminosity of the galaxy. e. can be used to determine the recessional velocity of a galaxy.