If we compare the Canadian natural unemployment rate to the U.S. natural unemployment rate, we find that for most years since 1980
A) the Canadian rate is higher, possibly the result of higher unemployment benefits in the United States for most of those years.
B) the U.S. rate is higher, possibly the result of greater job search within a larger country.
C) they are essentially the same because we have a lot in common.
D) the Canadian rate is higher, possibly the result of higher unemployment benefits in Canada for most of those years.
E) The U.S. rate is higher, possibly the result of more structural change occurring in the United States.
D
You might also like to view...
If the market in the figure above is a monopoly that maximizes its profit and charges every consumer the same price for each unit of output the consumer buys, the consumer surplus is equal to ________.
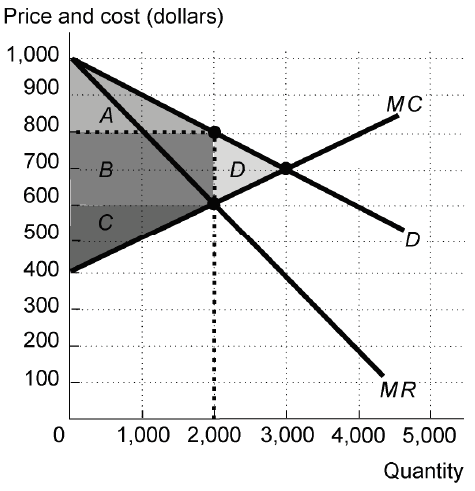
A) area A.
B) area B.
C) area C.
D) area D.
If an industry's long-run average total cost curve has an extended range of constant returns to scale, this implies that:
A. technology precludes both economies and diseconomies of scale. B. the industry will be a natural monopoly. C. both relatively small and relatively large firms can be viable in the industry. D. the industry will be comprised of a very large number of small firms.
In a perfectly competitive market, if P < MC, then
A. too much output is being produced. B. production is efficient, as the firm is earning profits. C. the firm is paying a price for resources that is too high. D. too little output is being produced.
Refer to the diagram. At output level Q:
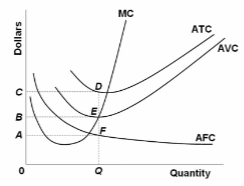
A. marginal product is falling.
B. marginal product is rising.
C. marginal product is negative.
D. one cannot determine whether marginal product is falling or rising.