Consumption + the change in net worth =
A. saving.
B. depreciation.
C. total assets.
D. economic income.
Answer: D
You might also like to view...
Total cost is equal to
a. TFC + TVC. b. TFC – TVC. c. TFC/TVC. d. TVC/TFC.
Refer to the following indifference map for a consumer who has an income of $48 to spend on goods X and Y and the market prices of X and Y are both $4: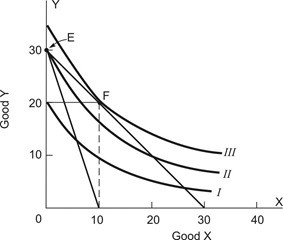 After the price of good X increases to $12 while the price of good Y remains $4, how many units of good X would be purchased?
After the price of good X increases to $12 while the price of good Y remains $4, how many units of good X would be purchased?
A. 0 B. 2 C. 4 D. 8 E. 12
Part of the normal aftermath of a period of excessive aggregate demand is
A. improvement in the quality of life. B. reflation. C. real GDP growth. D. stagflation. E. All of these responses are correct.
A perfectly competitive firm faces a market clearing price of $150 per unit. Average variable costs are at the minimum value of $200 per unit at an output rate of 100 units. Marginal cost equals $150 per unit at an output rate of 75 units. It can be concluded that the short-run profit-maximizing output rate is
A. 75 units, at which the firm earns $50 in economic profits per unit sold. B. 75 units, at which the firm earns zero economic profits per unit sold. C. 0 units, because price is less than average variable costs. D. 100 units, because marginal cost equals average variable costs.