If a firm stops production, then its:
A. fixed costs rise.
B. total costs may increase or decrease.
C. variable costs drop to zero.
D. All of these are true.
C. variable costs drop to zero.
You might also like to view...
In what way is monopolistic competition superior to perfect competition?
a. The cost of producing the industry's output is lower in monopolistic competition. b. Consumers benefit from having differentiated products instead of identical products. c. Long-run profits are higher in monopolistic competition than in pure competition. d. In monopolistic competition, firms can fully exploit any existing economies of scale.
In the short run, a firm's marginal cost tends to rise as more is produced because of
a. diminishing marginal returns. b. the implicit costs of production. c. diseconomies of scale. d. rising input costs.
A unit-elastic demand curve never touches or crosses either of the axes. Why?
What will be an ideal response?
Exhibit 10-8 Aggregate demand and supply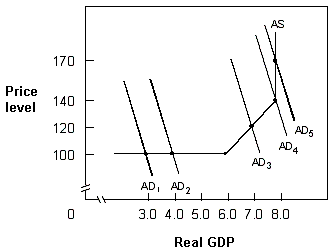
A. cost-push inflation. B. cost-pull inflation. C. demand-push inflation. D. demand-pull inflation.