Assume product A is an input in the production of product B. In turn, product B is a complement to product C. We can expect a decrease in the price of A to:
A. increase the supply of B and increase the demand for C.
B. decrease the supply of B and increase the demand for C.
C. decrease the supply of B and decrease the demand for C.
D. increase the supply of B and decrease the demand for C.
Answer: A
You might also like to view...
Starting from long-run equilibrium, a war that raises government purchases results in ________ output in the short run and ________ output in the long run.
A. lower; potential B. higher; potential C. higher; higher D. lower; higher
Suppose two people with the same level of income and wealth have different discount rates. Joe has a very high discount rate and Jim has a very low discount rate. Which one of the following is TRUE?
A) Joe is more likely to borrow than Jim. B) Joe is less likely to borrow than Jim. C) Joe and Jim will borrow the same amount. D) Neither Joe nor Jim would be borrowers.
If inflationary expectations increase, we can infer that: a. unemployment is above the natural rate
b. the economy is not on the long-run Phillips curve. c. the short-run Phillips curve is shifting to the left. d. output is below potential GDP. e. the unemployment rate is at the natural rate.
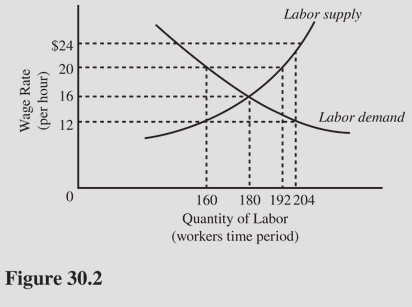 In Figure 30.2, the equilibrium wage rate is
In Figure 30.2, the equilibrium wage rate is
A. $20 per hour. B. $12 per hour. C. $24 per hour. D. $16 per hour.