If a firm enjoys producer surplus in perfectly competitive Market A of $1000 and would enjoy producer surplus in perfectly competitive Market B of $1200, the firm would consider moving to Market B if
A) fixed costs are greater than $100 in Market A.
B) fixed costs are less than $200 in Market B.
C) fixed costs are less than $300 but greater than $200 in Market B.
D) fixed costs in Market B are less than the fixed costs in Market A plus $200.
D
You might also like to view...
A market's equilibrium is the point at which the supply and demand curves intersect
a. True b. False Indicate whether the statement is true or false
Given the slower growth in the demand for labor in the United States since 1973, the large increases in employment must be the result of:
A. decreases in the demand of labor. B. increases in the real wage. C. increases in the supply of labor. D. decreases in the supply of labor.
Use the following graph, which shows the supply and demand for British pounds, to answer the next question.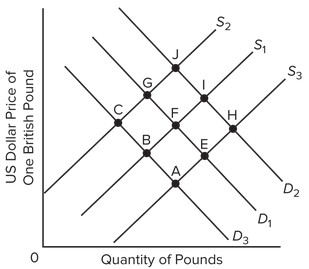 D1 and S1 represent the initial demand and supply curves. If there is a large increase in the number of American tourists visiting Britain because of a major event (like the Olympics or the World Cup), what should the British government do if it wants to fix the exchange rate at its initial level?
D1 and S1 represent the initial demand and supply curves. If there is a large increase in the number of American tourists visiting Britain because of a major event (like the Olympics or the World Cup), what should the British government do if it wants to fix the exchange rate at its initial level?
A. Shift D1 to D3 B. Shift S1 to S2 C. Shift S1 to S3 D. Shift D1 to D2
Suppose buyers in the used car market are willing to pay $4,000 for a plum (high-quality) used car and $2,000 for a lemon (low-quality) used car. If buyers believe that 50% of the used cars on the market are lemons (low quality), what would they be willing to pay for a used car?
A. $2000 B. $3000 C. $3500 D. $4000