John is buying a scented candle for his girlfriend. John thinks about her flower-scented perfume, flower-scented air spray, and flower-scented shampoo. He decides to buy her a flower-scented candle. His behavior is:
A. using a heuristic called a rule of thumb.
B. an example of the endowment effect because she already has flower-scented goods.
C. an example of loss aversion because he doesn't want to make the wrong choice.
D. an example of status quo bias because he doesn't want to deviate from her normal choice of scent.
A. using a heuristic called a rule of thumb.
You might also like to view...
Use the following graphs to answer the next question.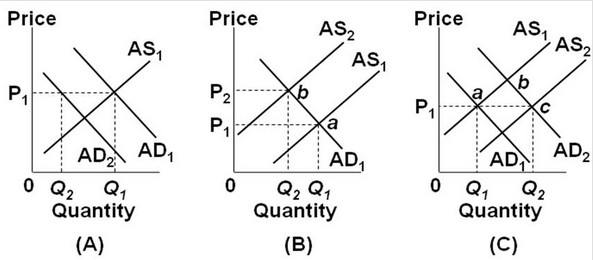 In the diagrams above, AD1 and AS1 represent the initial state of an economy. If full-employment output is at Q2, which diagram represents the adjustment back to full employment output in the absence of government intervention? ________.
In the diagrams above, AD1 and AS1 represent the initial state of an economy. If full-employment output is at Q2, which diagram represents the adjustment back to full employment output in the absence of government intervention? ________.
A. panel (A) only B. panel (B) only C. panel (C) only D. panels (B) and (C)
The deadweight loss associated with producing a product that has an external cost occurs because
A) too much output is produced. B) too little output is produced. C) the price that firms charge for the good is too high. D) not enough resources are allocated to producing the good. E) the marginal social cost does not equal zero.
A monopolist is defined as
A. a single producer of a good or service for which there is no close substitute. B. a producer of a good or service that is expensive to produce, requiring large amounts of capital equipment. C. a large firm, making substantial profits, that is able to make other firms do what it wants. D. a firm with many business establishments located across the nations.
The production possibility frontier is a graph that shows
A. all the combinations of goods and services that are consumed over time if all of society's resources are used efficiently. B. the rate at which an economy's output will grow over time if all resources are used efficiently. C. the amount of goods and services consumed at various average price levels. D. all the combinations of goods and services that can be produced if all of society's resources are used efficiently.