Study the chart of the mating seasons of these five species of frogs. What factor keeps the frogs reproductively isolated? What other factors may be involved? 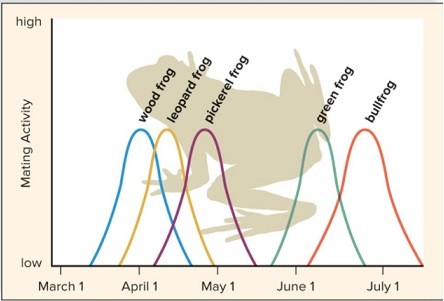
What will be an ideal response?
Answers may vary. This chart obviously describes how the mating seasons of the frogs is one factor in maintaining reproductive isolation. The wood, leopard, and pickerel frogs do not mate at the same time of year as the green frog and bullfrog and there is, therefore, very little chance of hybridization occurring. This is a good example of temporal isolation. There is, however, overlap in the mating seasons of the wood, leopard, and pickerel frogs, as well as the green frog and bullfrog. This situation suggests that other factors may be involved, such as occupying different habitats.
You might also like to view...
Using fetal DNA from the mother’s blood for prenatal testing is a noninvasive procedure
a. True b. False
Which muscle cells are designed for endurance?
A) slow-twitch cells B) fast-twitch cells C) myoglobin D) hemoglobin
Natural killer cells
A) engulf and destroy invading bacteria. B) are located on the surface of the skin. C) destroy body cells that have been invaded by viruses. D) are a type of lymphocyte. E) produce secretions that inhibit the growth of pathogenic microbes.
In the laboratory, fruit flies (Drosophila) were artificially selected for the number of bristles on their bodies. One population (R) was selected for low numbers of bristles, a second population (S) for high numbers of bristles.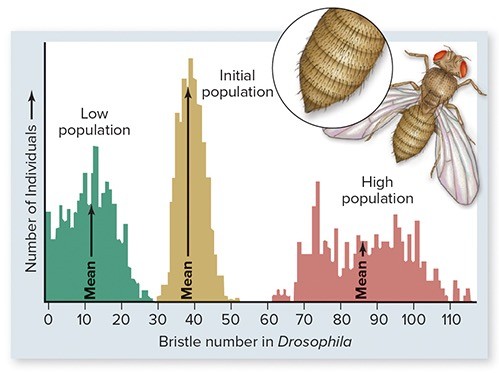 In order for the scientists to artificially select Drosophila for their number of bristles,
In order for the scientists to artificially select Drosophila for their number of bristles,
A. they had to induce mutations into their populations of Drosophila. B. genetic variation had to be present in the population. C. the number of bristles in each Drosophila had to be random. D. dramatic mutations had to be produced by the selection. E. they had to study the population for millions of years.