An observer moving with a light clock in a spaceship sees a light flash bouncing up and down between parallel mirrors in 1 nanosecond. An observer at rest outside the spaceship sees the same up-and-down flash in
A) 1 nanosecond also.
B) less than 1 nanosecond.
C) more than 1 nanosecond.
Answer: C
You might also like to view...
Doubling the diameter of a loop of wire produces what change of induced emf?
A. The induced emf is 4 times as much. B. The induced emf is twice as much. C. There is no change in the induced emf. D. The induced emf is 6.28 times as much.
Force on a Wire: A wire in the shape of an "M" lies in the plane of the paper. It carries a current of 2.0 A, flowing from A to E, as shown in the figure. It is placed in a uniform magnetic field of 0.75 T in the same plane, directed as shown on the right side of the figure. The figure indicates the dimensions of the wire. Note that AB is parallel to DE and to the baseline from which the magnetic field direction is measured. What are the magnitude and direction of the force acting on section AB of this wire?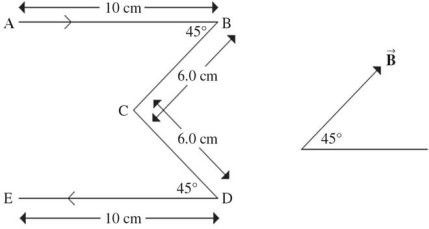
A. 0.20 N perpendicular out of the page B. 0.40 N perpendicular out of the page C. 0.11 N perpendicular out of the page D. 0.20 N perpendicular into the page E. 0.11 N perpendicular into the page
According to recent estimates, genetic contributions to the development of most psychological disorders are _________. *
Fill in the blank(s) with the appropriate word(s).
Black holes cannot be observed directly, because they emit no light. However, a scientist can hunt for black holes because
A. a black hole will reflect light. B. magnetic fields cause an emanation of thermal energy in the form of high-speed protons. C. a black hole can still emit electrons. D. black holes can gravitationally influence the orbits of nearby stars, and those stars can be observed.