A monopolist faces
A) a downward-sloping demand curve. B) a horizontal demand curve.
C) a perfectly elastic demand curve. D) a perfectly inelastic demand curve.
A
You might also like to view...
A major loophole was punched through the McFadden Act as banks
A) formed bank holding companies. B) developed negotiable certificates of deposit. C) began paying interest on checkable deposits. D) converted themselves into savings-and-loans.
Which of the following assumptions indicates that there is no trade-off between inflation and unemployment?
A) A vertical aggregate demand curve B) A vertical Phillips Curve C) Constant velocity D) Constant money supply growth rate
Economic growth is represented by a: a. leftward shift of a production possibilities curve
b. rightward shift of the long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS). c. horizontal long-run aggregate supply curve (LRAS). d. downward shift of an aggregate production function.
Figure 9-6 shows the marginal cost and average total cost curves for a perfectly competitive firm. This firm will
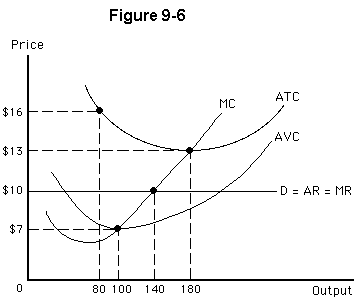
a.
earn an economic profit
b.
suffer an economic loss in this long-run situation
c.
suffer an economic loss in the short run and close
d.
break even if it expands to 180 units of output
e.
suffer an economic loss and continue producing in the short run